How to Use setFont in Java
-
Using
setFont()andFontObject Method -
Using
setFont()andgetFont().deriveFont()to Set a Style in the Existing Font -
Using
setFont()andFont.createFont()to Set a Custom Font - Conclusion

In this article, we will learn how we can use the setFont() method, a function that sets the font to the components of JFrame.
One of the key elements in shaping the visual identity of GUI components is the font they use. The setFont() method in Java, particularly when combined with the creation of Font objects, offers a powerful mechanism for customizing the font characteristics of various components.
Java’s setFont() method empowers developers to dynamically set the font of a component, providing a means to tailor the application’s look and feel.
Using setFont() and Font Object Method
The setFont() is a method used in programming, specifically with graphical user interfaces or text rendering. It sets the font style for displaying text.
The associated font object method allows customization of text appearance, such as font size and type. Together, they enable developers to control the visual aspects of text within applications, providing flexibility and enhancing user experience.
There are different ways of setting the font for a graphical component in Java.
| Syntax | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
component.setFont(Font font); |
font: A Font object representing the font that you want to set for the component. |
This syntax sets the font of the component directly using a specified Font object. |
component.setFont(new Font(fontFamily, style, size)); |
-fontFamily: A string representing the font family (e.g., Arial).- style: An integer constant representing the font style (e.g., Font.PLAIN, Font.BOLD, Font.ITALIC).- size: A float representing the font size (e.g., 12.0f). |
This syntax involves creating a Font object inline and setting it as the font for the component. It allows customization of font family, style, and size in a single line of code. |
When setting the font style using setFont(), you can use constants to specify the desired style for the text in your graphical components. These constants are part of the Font class in Java (java.awt.Font).
Adjust the style according to your visual preferences and design requirements.
Here’s a table summarizing various font styles that can be used with the setFont() method in Java:
| Font Style Constant | Description |
|---|---|
Font.PLAIN |
Plain (no style) |
Font.BOLD |
Bold |
Font.ITALIC |
Italic |
Font.BOLD + Font.ITALIC |
Bold and Italic |
Let’s delve into a practical example to illustrate how to leverage the setFont() method with a Font object.
Consider a scenario where we have a JLabel that we want to customize with a specific font. We’ll use a Font object to define the font and then apply it to the JLabel.
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class FontExample extends JFrame {
public FontExample() {
initComponents();
}
private void initComponents() {
// Create a JLabel
JLabel textLabel = new JLabel("Hello, Font World!");
// Create a Font object with desired properties
Font customFont = new Font("Arial", Font.BOLD, 18);
// Set the font of the JLabel using setFont()
textLabel.setFont(customFont);
// Add the JLabel to the frame
add(textLabel);
// Frame configuration
setTitle("Font Example");
setSize(300, 150);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> { new FontExample().setVisible(true); });
}
}
In our FontExample class extending JFrame, the initComponents method orchestrates the setup of GUI elements.
We begin by creating a JLabel, textLabel, initialized with the text Hello, Font World!.
Next, we fashion a Font object, customFont, utilizing the Font constructor. This font is tailored with the Arial typeface, bold (Font.BOLD), and a size of 18.
The setFont() method is then employed on textLabel to implement our custom font.
The remaining code handles typical frame configuration, including title, size, close operation, and centering on the screen.
Output:
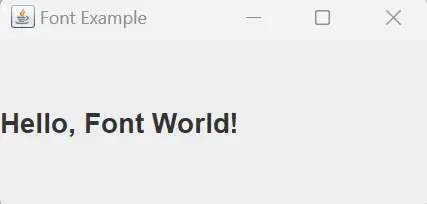
Upon running this program, a JFrame window titled Font Example will appear, showcasing the JLabel with the custom font. The text Hello, Font World! will be rendered in bold, using the specified Arial font and a font size of 18.
Using setFont() and getFont().deriveFont() to Set a Style in the Existing Font
The setFont() is a programming method to set the font style, while getFont().deriveFont() is used to create a modified version of the current font.
Developers use setFont() to define the initial font and getFont().deriveFont() to make variations like adjusting size or style without altering the original. This duo enhances text customization in applications, offering a simple way to control and adapt font properties dynamically.
Example:
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class FontCustomizationExample extends JFrame {
public FontCustomizationExample() {
initComponents();
}
private void initComponents() {
// Create a JLabel
JLabel textLabel = new JLabel("Hello, Font World!");
// Get the default font of the label
Font currentFont = textLabel.getFont();
// Derive a new font with modified size
Font modifiedFont = currentFont.deriveFont(Font.ITALIC, 24.0f);
// Set the modified font using setFont()
textLabel.setFont(modifiedFont);
// Add the JLabel to the frame
add(textLabel);
// Frame configuration
setTitle("Font Customization Example");
setSize(300, 150);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> { new FontCustomizationExample().setVisible(true); });
}
}
Creating a JLabel named textLabel initializes it with the initial text.
Obtain the current font of the textLabel using getFont().
Next, using deriveFont() on currentFont, a modified font named modifiedFont is derived, italicizing the text (Font.ITALIC) and setting its size to 24.0.
Applying this modified font to textLabel using setFont() dynamically changes its appearance.
The remaining code manages standard frame setup, incorporating textLabel and configuring the frame’s properties.
Upon running this example, a JFrame window titled Font Customization Example will appear, showcasing the JLabel with the original text Hello, Font World! but with a customized font size of 24.0.
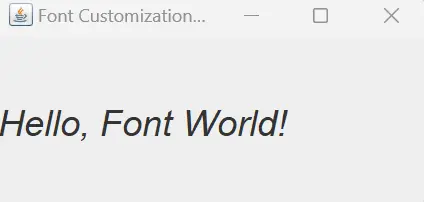
This dynamic approach allows for seamless adjustments to the font without losing the original font properties, illustrating the power of combining setFont() and getFont().deriveFont().
Using setFont() and Font.createFont() to Set a Custom Font
The Font.createFont() is used to dynamically load and create a font instance from an external font file.
Using setFont() and Font.createFont() together empowers developers to establish and customize text appearances in applications. The setFont() handles existing system fonts, while Font.createFont() extends the range by enabling the use of external font resources, expanding design possibilities.
Java provides developers with powerful tools for font customization, and among them are the setFont() method and the lesser-explored Font.createFont() method.
Example:
import java.awt.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.swing.*;
public class FontCustomizationExample extends JFrame {
public FontCustomizationExample() {
initComponents();
}
private void initComponents() {
// Create a JLabel
JLabel textLabel = new JLabel("Hello, Font World!");
// Set font using createFont()
try {
Font customFont = Font.createFont(Font.TRUETYPE_FONT, new File("path/to/customFont.ttf"))
.deriveFont(Font.BOLD, 18.0f);
textLabel.setFont(customFont);
} catch (FontFormatException | IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Add the JLabel to the frame
add(textLabel);
// Frame configuration
setTitle("Font Customization Example");
setSize(300, 150);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> { new FontCustomizationExample().setVisible(true); });
}
}
We begin by creating a JLabel named textLabel with the initial text.
Moving to font customization, we utilize the Font.createFont() method, dynamically loading a TrueType font file. Subsequently, we derive a modified font, enhancing its boldness and fixing the size at 18.0.
The remaining code ensures standard frame setup, adding textLabel and configuring the frame’s properties.
Upon execution, this example produces a JFrame window titled Font Customization Example that showcases the JLabel with the text Hello, Font World! styled with a custom font dynamically loaded using Font.createFont().

This synthesis of setFont() and Font.createFont() demonstrates the capability to seamlessly integrate static and dynamic font customization, providing developers with a versatile approach to meet diverse design requirements in their Java GUI applications.
Conclusion
The interplay of the setFont() method and the Font object in Java offers a versatile toolkit for crafting visually appealing and customized user interfaces. Experimenting with various font styles, sizes, and typefaces enhances the visual impact of GUIs, providing developers with a vast array of possibilities.
Combining the static approach of setFont() with the dynamic nature of getFont().deriveFont() and Font.createFont() further expands these possibilities, allowing developers to strike a harmonious balance between simplicity and versatility in font customization. The result is a powerful capability to create responsive and user-friendly interfaces that delight end-users.
Rupam Saini is an android developer, who also works sometimes as a web developer., He likes to read books and write about various things.
LinkedInRelated Article - Java Swing
- How to Clear Text Field in Java
- How to Create Canvas Using Java Swing
- How to Use of SwingUtilities.invokeLater() in Java
- How to Center a JLabel in Swing
- How to Change the JLabel Text in Java Swing
- Java Swing Date
