How to Add ActionListener to JButton in Java
-
ActionListenerto aJButton -
Add
ActionListenerto aJButtonUsing an Anonymous Inner Class -
Add
ActionListenertoJButtonUsing Lambda -
Add
ActionListenertoJButtonUsing Inheritance -
Best Practices and Tips Implementing
ActionListenerWithJButton - Conclusion

This article delves into implementing ActionListener for buttons in Java, detailing methods to add functionality, and explores best practices for efficient event handling.
ActionListener to a JButton
In Java, an ActionListener is an interface used with JButton to detect and respond to button clicks. When a JButton is clicked, the ActionListener’s actionPerformed method is triggered, allowing you to specify the actions or code to be executed in response to the button press.
This mechanism enables interactivity in graphical user interfaces (GUIs) by providing a way to handle user-initiated events. ActionListener is crucial for designing responsive and interactive applications, allowing developers to define behavior associated with button clicks, enhancing user experience by enabling dynamic responses to user input.
Add ActionListener to a JButton Using an Anonymous Inner Class
Adding ActionListener with anonymous class in Java is crucial for simplicity and brevity. It allows defining event-handling logic directly, reducing code verbosity compared to creating a separate class.
This method is ideal for quick, one-off implementations, promoting concise code without the need for extensive class structures.
Code Example:
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.*;
public class ButtonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a JFrame
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Button Example");
// Create a JButton
JButton clickButton = new JButton("Click Me");
// Add ActionListener using an anonymous inner class
clickButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// Code to be executed when the button is clicked
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Button Clicked!");
}
});
// Add the button to the frame
frame.getContentPane().add(clickButton);
// Set frame properties
frame.setSize(300, 200);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
In our Java Swing GUI application, we start by importing necessary packages for Swing components and the ActionListener interface. The main method begins with the creation of a JFrame, serving as the primary window.
We then proceed to create a JButton named clickButton with the label Click Me. The key step involves adding an ActionListener to the button using an anonymous inner class.
Within this class, the actionPerformed method specifies the code to be executed when the button is clicked. Subsequently, we add the button to the content pane of the JFrame, and finally, we set the frame’s properties, including its size, default close operation, and visibility.
This concise and structured approach ensures that our GUI application responds appropriately when the user clicks the Click Me button.
Output:
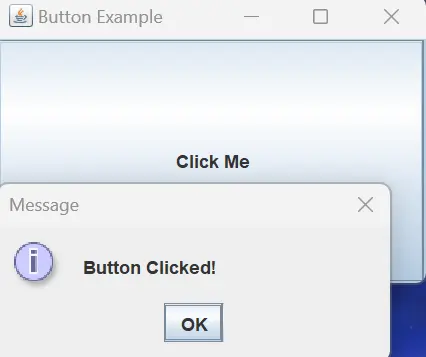
When you run this code and click the Click Me button, a dialog with the message Button Clicked! will appear. This demonstrates the successful integration of the ActionListener using an anonymous inner class, allowing us to respond dynamically to button clicks in our Java GUI application.
Add ActionListener to JButton Using Lambda
Adding ActionListener with lambda expressions in Java simplifies code by offering a concise syntax. It enhances readability and reduces boilerplate, making the code more expressive and maintainable.
This method streamlines the code, making it more readable and reducing boilerplate while still achieving the same result of executing specific actions when the button is clicked.
Code Example:
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import javax.swing.*;
public class LambdaButtonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a JFrame
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Lambda Button Example");
// Create a JButton
JButton clickButton = new JButton("Click Me");
// Add ActionListener using lambda expression
clickButton.addActionListener(e -> {
// Code to be executed when the button is clicked
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Button Clicked!");
});
// Add the button to the frame
frame.getContentPane().add(clickButton);
// Set frame properties
frame.setSize(300, 200);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
In our Java Swing GUI application, we start by importing necessary packages for Swing components and the ActionEvent class. The main method begins with the creation of a JFrame, serving as the primary window.
We then proceed to create a JButton named clickButton with the label Click Me. The innovative step involves adding an ActionListener to the button using a lambda expression.
This concise expression replaces the traditional anonymous inner class, succinctly defining the actionPerformed method and specifying the code to be executed when the Click Me button is clicked. Following this, we add the button to the content pane of the JFrame, and finally, we set the frame’s properties, including its size, default close operation, and visibility.
This streamlined approach maintains the responsiveness of our GUI application to user clicks while enhancing code readability.
Output:
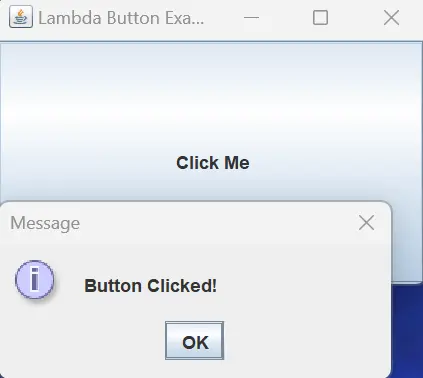
When you run this code and click the Click Me button, a dialog with the message Button Clicked! will appear. The use of lambda expressions enhances the readability of the ActionListener implementation, making the code concise and expressive while maintaining the functionality of responding to button clicks in our Java GUI application.
Add ActionListener to JButton Using Inheritance
Adding ActionListener with inheritance in Java promotes a structured and reusable approach. It encapsulates event-handling logic in a custom class, enhancing code organization and maintainability.
This method ensures a clean separation of concerns, making it easier to manage and extend functionality in larger applications.
Code Example:
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.*;
// Custom ActionListener class inheriting ActionListener interface
class CustomButtonListener implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// Code to be executed when the button is clicked
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Button Clicked!");
}
}
public class InheritanceButtonExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a JFrame
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Inheritance Button Example");
// Create a JButton
JButton clickButton = new JButton("Click Me");
// Create an instance of CustomButtonListener and attach it to the button
CustomButtonListener buttonListener = new CustomButtonListener();
clickButton.addActionListener(buttonListener);
// Add the button to the frame
frame.getContentPane().add(clickButton);
// Set frame properties
frame.setSize(300, 200);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
In our Java Swing GUI application, we begin by importing the necessary packages for Swing components and the ActionListener interface. To handle button click events, we introduce a custom class named CustomButtonListener that inherits the ActionListener interface and implements the actionPerformed method.
This class encapsulates the specific actions to be executed when the button is clicked. Moving on to the main method, we create a JFrame, serving as the primary window for our application.
Subsequently, we instantiate a JButton named clickButton with the label Click Me. The unique aspect of this approach involves attaching an instance of our custom ActionListener class to the button, establishing a clean and organized event handling structure.
The button is then added to the content pane of the JFrame. Lastly, we set essential frame properties, including its size, default close operation, and visibility.
Output:
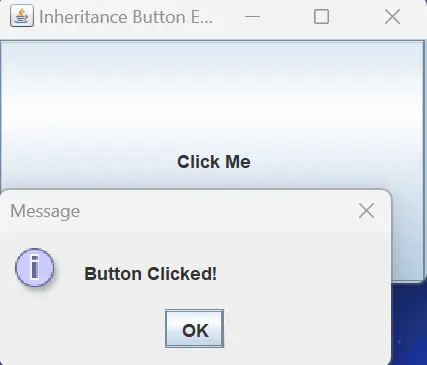
Running this code and clicking the Click Me button will result in a dialog displaying the message Button Clicked! This inheritance-based method offers a structured and reusable approach to handling button click events, contributing to the clarity and efficiency of Java GUI applications.
Best Practices and Tips Implementing ActionListener With JButton
Clear and Descriptive Naming
Use meaningful names for buttons and ActionListener methods to enhance code readability.
Separation of Concerns
Maintain a clean separation of concerns by keeping ActionListener logic separate from the GUI code.
Reusable ActionListener Classes
Consider creating reusable custom classes that implement ActionListener for more complex applications.
Documentation
Include comments or documentation to explain the purpose and functionality of ActionListener implementations.
Error Handling
Implement appropriate error handling within ActionListener methods to handle unexpected scenarios.
Consistency Across UI
Maintain consistency in ActionListener implementation across buttons in the user interface.
Testing and Debugging
Thoroughly test and debug ActionListener implementations to ensure correct behavior and responsiveness.
Use of Final Variables
Consider using final variables for components and values within ActionListener to enhance code stability.
User Feedback
Provide user feedback, such as visual cues or messages, to indicate button click success or failure.
Conclusion
Mastering ActionListener implementations in Java for JButton handling is crucial for effective GUI programming. This article has delved into various approaches—anonymous inner classes, lambda expressions, and inheritance—offering diverse methods to cater to different coding preferences and project requirements.
Understanding these techniques empowers developers to craft responsive and organized event handling for buttons, optimizing code readability and maintainability. Choosing the right method—whether for simplicity, brevity, or scalability—provides a solid foundation for creating intuitive and user-friendly Java GUI applications.
By exploring these ActionListener methods and their nuances, developers gain the flexibility to tailor their approach, improving the quality and efficiency of their code while ensuring seamless interactivity in their graphical interfaces.
Rupam Saini is an android developer, who also works sometimes as a web developer., He likes to read books and write about various things.
LinkedInRelated Article - Java Swing
- How to Clear Text Field in Java
- How to Create Canvas Using Java Swing
- How to Use of SwingUtilities.invokeLater() in Java
- How to Center a JLabel in Swing
- How to Change the JLabel Text in Java Swing
- Java Swing Date
