Long.MAX_VALUE in Java
In programming, different data types serve distinct purposes, and one of the most critical aspects is their range.
When working with numerical values, choosing the right data type can make a substantial difference, especially when dealing with colossal numbers. This is where the long data type in Java comes into play.
A long is used when you require a vast range of values, although it comes at the cost of increased memory usage. But what if you need to assign a variable the maximum value it can hold?
This is where Java’s Long.MAX_VALUE constant becomes invaluable.
Long.MAX_VALUE in Java
Before we dive deeper into the world of Long.MAX_VALUE, let’s gain a better understanding of the long data type itself. In Java, a long is a 64-bit signed two’s complement integer, which means it can represent both positive and negative whole numbers.
Its value range is expansive, spanning from -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807. This makes the long data type the go-to choice for handling large numerical computations, such as timestamps, unique identifiers, or other scenarios that require extensive numerical precision.
Long.MAX_VALUE is a public static constant variable of type long that resides within the Long class of the Java Standard Library. Its primary function is to represent the maximum value that a variable of type long can hold, and this value is truly staggering.
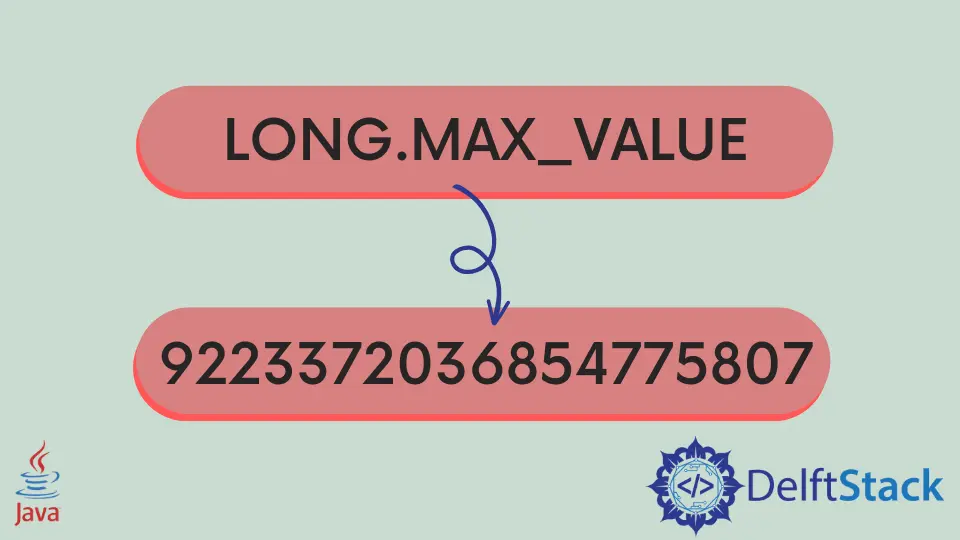
Long.MAX_VALUE equates to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807, a number that is incredibly significant when you need to work with the largest possible long integer without the concerns of overflow.
Use Cases of Long.MAX_VALUE in Java
Now that we’ve grasped the importance of Long.MAX_VALUE, let’s explore how it can be effectively utilized in your Java programs:
Loop Termination
When you need to iterate through a range of long integers, you can use Long.MAX_VALUE as a termination condition. This allows you to search for a value without worrying about an upper limit.
For instance, if you want to find a specific number in a range of long values, you can utilize a loop like this:
public class LongRangeSearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long target = 9999999999L; // Replace this with your target value
boolean targetFound = false;
for (long i = 0; i <= Long.MAX_VALUE; i++) {
if (i == target) {
System.out.println("Target value " + target + " found!");
targetFound = true;
break;
}
}
if (!targetFound) {
System.out.println("Target value " + target + " not found in the search range.");
}
}
}
Output:
Target value 9999999999 found!
In this code example, we initialize the target variable with a specific value (in this case, 9,999,999,999). You can replace this value with the number you want to find within the range.
We then use a for loop to iterate through a range of long integers, starting from 0 and incrementing up to Long.MAX_VALUE. Inside the loop, we check if the current value (i) is equal to the target value.
When a match is found, we print a message indicating the successful execution and set the targetFound variable to true. Then, we use the break statement to exit the loop once the target value is found.
After the loop, we check the value of targetFound. If it is false, we print a message indicating that the target value was not found within the search range.
Setting Default Values
Long.MAX_VALUE can also be employed as a placeholder when initializing variables that are meant to store the maximum value. This is particularly useful when you want to find the maximum value within a collection or array.
You can initialize a variable with Long.MIN_VALUE (the minimum value for long) and update it when you find a larger value. Here’s an example:
public class FindMaxValue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long[] longArray = {100, 200, 300, 400, 500, Long.MAX_VALUE, 600};
long max = Long.MIN_VALUE;
for (long value : longArray) {
if (value > max) {
max = value;
}
}
System.out.println("The maximum value in the array is: " + max);
}
}
In this code example, we create a long array, longArray, which contains a mix of values, including Long.MAX_VALUE and other positive integers.
We then initialize the max variable with Long.MIN_VALUE, which is the smallest possible long value. This sets the stage for comparing and finding larger values within the array.
Using a for loop, we iterate through the elements of longArray. Within this loop, we check if the current value is greater than the current max.
If it is, we update the max variable to store the larger value. After iterating through the entire array, we print a message indicating the maximum value found within the array.
Output:
The maximum value in the array is: 9223372036854775807
In this example, Long.MAX_VALUE is used to initialize max, and the loop efficiently identifies the largest value in the array, showcasing the utility of Long.MAX_VALUE as a sentinel value for finding maximum values within collections.
Checking for Overflow
To ensure that your arithmetic operations do not result in overflow, you can compare the result with Long.MAX_VALUE. If the result is greater than Long.MAX_VALUE, it is a clear indication that an overflow condition has occurred.
This comparison allows you to take appropriate measures to handle the situation, such as adjusting the data type, using a larger data type, or reevaluating your algorithm.
Here’s an example code snippet that demonstrates how to use Long.MAX_VALUE to check for overflow in arithmetic operations with long integers:
public class OverflowDetectionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long a = Long.MAX_VALUE; // Set a to the maximum value for a long
long b = 1; // Add 1 to the maximum value
long sum = a - b;
if (sum < a || sum > Long.MAX_VALUE) {
System.out.println("Overflow detected!");
} else {
System.out.println("No overflow");
System.out.println("Sum: " + sum);
}
}
}
In this example, we first set a to the maximum value for a long using Long.MAX_VALUE.
Then, we attempt to add 1 to a. Before performing the addition, we check if the result is less than the original value of a or greater than Long.MAX_VALUE.
If this condition is true, it indicates that an overflow has occurred. Otherwise, the addition is within the valid range for long values and no overflow has occurred.
Output:
Overflow detected!
In Java, attempting to add 1 to the Long.MAX_VALUE constant will indeed result in overflow, causing the value to wrap around to the lowest possible long value, which is -9223372036854775808.
This behavior is a consequence of the fixed range of values that the long data type can hold, and when you exceed that range, it wraps around to the other end of the spectrum.
Additional Example on the Use of Long.MAX_VALUE in Java
Here is an additional example demonstrating the use of Long.MAX_VALUE in Java in checking if a value is within the long range.
You can use Long.MAX_VALUE to verify if a given value is within the valid range for the long data type. This is particularly useful when reading user input or data from an external source.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LongRangeCheck {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
try {
long userInput = scanner.nextLong();
if (userInput >= Long.MIN_VALUE && userInput <= Long.MAX_VALUE) {
System.out.println("Valid long value: " + userInput);
} else {
System.out.println("Input is outside the valid long range.");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Invalid input. Please enter a valid long value.");
}
}
}
In this Java program, which we’ve named LongRangeCheck, we’re building a tool that interacts with users through the console.
The program first prompts users to input a number. To read this input, we use a handy Java class called Scanner.
Once the user enters a number, we try to convert it into a long data type.
Now, there’s a range of values that a long can hold. It ranges from the smallest possible long value, known as Long.MIN_VALUE, to the largest possible long value, known as Long.MAX_VALUE.
If the user’s input falls within this range, we tell them it’s a Valid long value and show them what they entered. But, if it’s outside of this range or if it’s not a number at all, we’ve got a backup plan.
We catch any exceptions that might occur, which usually means the input was invalid, and we politely inform the user to enter a valid long value.
So, in a nutshell, LongRangeCheck is a simple program that makes sure user inputs are valid long values and lets users know if they’re within the permissible range.
Conclusion
In summary, Long.MAX_VALUE plays an important role in Java programming, allowing developers to work with the maximum possible long integer value without the constant concern of overflow. Whether you’re iterating through vast ranges, setting default values, or verifying overflow conditions, this constant simplifies and enhances the precision of numerical operations in Java.
By understanding its significance and knowing how to use it effectively, you can harness the full potential of the long data type, empowering you to tackle complex numeric computations with confidence and precision.