Difference Between i++ and ++i Operators in Java
-
Pre-Increment (
++i) Operator in Java -
Post-Increment (
i++) Operator in Java -
Difference Between
i++and++iOperators in Java -
Understanding Pre-Increment (
++i) and Post-Increment (i++) Operator in Java - Conclusion
This tutorial introduces differences between the pre-increment, ++i, and post-increment, i++, operators in Java.
In Java, the ++i and i++ operators are known as increment operators. The ++i is known as the pre-increment operator, while the i++ operator is known as the post-increment operator.
There are several ways to use these operators, such as in the loop for increment the loop conditional variable and iterate all the elements of a List in Java. For example, the for loop, the for-each loop, the forEach() method with list or stream, etc.
Let’s see some examples.
Pre-Increment (++i) Operator in Java
The pre-increment operator (++i) in Java increases the value of a variable by 1 before its current value is used in an expression. It increments the variable and returns the updated value, effectively adding 1 to the original value during the operation.
Post-Increment (i++) Operator in Java
The post-increment operator (i++) in Java increases the value of a variable by 1 after its current value is used in an expression. It returns the original value and then increments the variable, effectively adding 1 to its value after the operation.
Difference Between i++ and ++i Operators in Java
In Java, both i++ and ++i are increment operators, but they are used in slightly different ways. Here are the main differences between the two:
| Aspect | i++ |
++i |
|---|---|---|
| Operand Value | Post-increment operator. Uses the current value of i and then increments it by 1. |
Pre-increment operator. Increments the value of i by 1 and then uses the updated value. |
| Expression Value | The value of the expression is the current value of i before the increment. |
The value of the expression is the updated value of i after the increment. |
| Usage in Expressions | Can be used in various expressions, such as assignments, conditionals, and loops. | Can be used in various expressions, similar to post-increment. |
| Return Type | Same return type as the variable they operate on (integral data types like int, long, etc.). | Same return type as the variable they operate on (integral data types like int, long, etc.). |
Examples:
// Operand Value
int i = 5;
int result1 = i++; // result1 is 5, i becomes 6
int result2 = ++i; // result2 is 7, i becomes 7
// Expression Value
int i = 5;
int result1 = i++; // result1 is 5, i becomes 6
int result2 = ++i; // result2 is 7, i becomes 7
// Usage in Expressions
int i = 5;
int result1 = i++; // result1 is 5, i becomes 6
int result2 = ++i; // result2 is 7, i becomes 7
int x = 10;
int y = x++; // y is 10, x becomes 11
int z = ++x; // z is 12, x becomes 12
// Return Type
int i = 5;
int result1 = i++; // result1 is 5, i becomes 6
long j = 10;
long result2 = ++j; // result2 is 11, j becomes 11
While both i++ and ++i increment the value of a variable, the key difference lies in when the increment takes place (before or after using the current value in an expression) and how the updated value is returned.
Understanding Pre-Increment (++i) and Post-Increment (i++) Operator in Java
In Java programming, the use of increment operators, specifically pre-increment (++i) and post-increment (i++), plays a crucial role in enhancing code flexibility and efficiency. These operators are employed to increment the value of a variable, but they do so in slightly different manners.
Let’s begin with a simple Java program that demonstrates the functionality of both pre-increment and post-increment operators.
public class IncrementExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 5;
int y, z;
// Using post-increment
y = x++;
// Using pre-increment
z = ++x;
// Displaying results
System.out.println("Post-Increment Result (y): " + y);
System.out.println("Pre-Increment Result (z): " + z);
}
}
To illustrate the difference between pre-increment and post-increment in Java, we initialize an integer variable, x, along with two additional variables, y and z, intended to store the results of subsequent increment operations.
The line y = x++; employs the post-increment operator, signifying that the current value of x is assigned to y, and only after this assignment does x undergo incrementation. Conversely, in the line z = ++x;, the pre-increment operator is utilized.
In this scenario, x is incremented first, and then the updated value is assigned to z. The program concludes by printing the results, offering insight into the impact of using post-increment and pre-increment in the context of the given example.
When we run this program, we’ll see the following output:
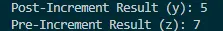
Post-Increment Result (y): 5
Pre-Increment Result (z): 7
Understanding the nuances between pre-increment and post-increment in Java is crucial for writing efficient and readable code. The choice between them depends on the specific requirements of a given task. Post-increment is useful when the original value is needed before incrementing, while pre-increment is handy when the updated value is immediately required.
By leveraging these increment operators effectively, Java developers can enhance the clarity and efficiency of their code.
Conclusion
The pre-increment (++i) and post-increment (i++) operators in Java serve as powerful tools for incrementing variables, each with its distinct behavior. The key distinction lies in when the increment occurs – pre-increment increments the value before usage, while post-increment does so afterward.
This subtle difference carries implications for code execution. Through a simple example, we’ve demonstrated how these operators impact variable values.
By understanding and judiciously applying pre-increment and post-increment, Java developers can enhance code efficiency and readability based on specific programming requirements.