How to Use RMSE in Python
- the Formula for Root Mean Square Error in Python
-
Calculate
RMSEUsingNumPyin Python -
Calculate
RMSEUsingscikit-learnLibrary in Python
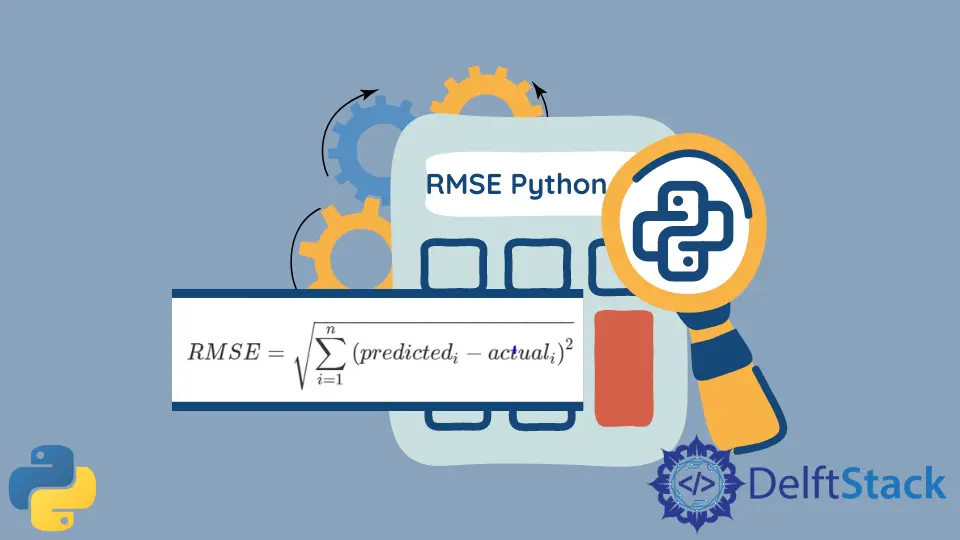
RMS (root mean square), also known as the quadratic mean, is the square root of the arithmetic mean of the squares of a series of numbers.
RMSE (root mean square error) gives us the difference between actual results and our calculated results from the model. It defines the quality of our model (which uses quantitative data), how accurate our model has predicted, or the percentage of error in our model.
RMSE is one of the methods for evaluating supervised machine learning models. The larger the RMSE will be the inaccuracy of our model and vice versa.
There are multiple ways to find the RMSE in Python by using the NumPy library or scikit-learn library.
the Formula for Root Mean Square Error in Python
The logic behind calculating the RMSE is through its following formula:
Calculate RMSE Using NumPy in Python
NumPy is a useful library for dealing with large data, numbers, arrays, and mathematical functions.
Using this library, we can easily calculate RMSE when given the actual and predicted values as an input. We will use the built-in functions of the NumPy library for performing different mathematical operations like square, mean, difference, and square root.
In the following example, we will calculate RMSE by first calculating the difference between actual and predicted values. We calculate the square of that difference, then take the mean.
Until this step, we will get the MSE. To get the RMSE, we will take the square root of MSE.
Example Code:
# python 3.x
import numpy as np
actual = [1, 2, 5, 2, 7, 5]
predicted = [1, 4, 2, 9, 8, 6]
diff = np.subtract(actual, predicted)
square = np.square(diff)
MSE = square.mean()
RMSE = np.sqrt(MSE)
print("Root Mean Square Error:", RMSE)
Output:
#python 3.x
Root Mean Square Error: 3.265986323710904
Calculate RMSE Using scikit-learn Library in Python
Another way to calculate RMSE in Python is by using the scikit-learn library.
scikit-learn is useful for machine learning. This library contains a module called sklearn.metrics containing the built-in mean_square_error function.
We will import the function from this module into our code and pass the actual and predicted values from the function call. The function will return the MSE. To calculate the RMSE, we will take MSE’s square root.
Example Code:
# python 3.x
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
import math
actual = [1, 2, 5, 2, 7, 5]
predicted = [1, 4, 2, 9, 8, 6]
MSE = mean_squared_error(actual, predicted)
RMSE = math.sqrt(MSE)
print("Root Mean Square Error:", RMSE)
Output:
#python 3.x
Root Mean Square Error: 3.265986323710904
I am Fariba Laiq from Pakistan. An android app developer, technical content writer, and coding instructor. Writing has always been one of my passions. I love to learn, implement and convey my knowledge to others.
LinkedIn