How to Print a Table in Java
- Importance of Printing a Table in Java
-
Using
System.out.printand Formatting to Print a Table in Java -
Using
StringBuilderto Print a Table in Java -
Using
Formatterto Print a Table in Java -
Using
PrintStreamto Print a Table in Java - Conclusion

This article explores the significance of printing tables in Java and delves into various methods to achieve this, emphasizing their importance and practical applications in presenting structured data efficiently.
Importance of Printing a Table in Java
Printing a table in Java is crucial for presenting structured data in a readable format. It enhances user understanding, facilitates data analysis, and improves the overall user experience in applications and command-line tools.
The formatted table provides a clear representation of information, aiding developers, administrators, and end-users in making informed decisions and interpreting data efficiently.
Using System.out.print and Formatting to Print a Table in Java
Using System.out.print and formatting in Java for table printing ensures a clean, organized, and visually appealing output. This method provides flexibility, avoids hardcoded values, and allows dynamic customization of table structure.
It simplifies code readability, making it an efficient choice for presenting tabular data in a clear and concise manner.
Let’s start by presenting a complete working code example that prints a well-formatted table in the console. This example will showcase a table with column and row separators represented by | and -, respectively.
The values in the table will be dynamic, avoiding hardcoded entries.
public class TablePrinter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
printTable(new String[] {"Name", "Age", "City"}, new String[] {"John Doe", "28", "New York"},
new String[] {"Jane Smith", "35", "San Francisco"},
new String[] {"Bob Johnson", "42", "Chicago"});
}
private static void printTable(String[] headers, String[]... data) {
int[] columnWidths = calculateColumnWidths(headers, data);
printHorizontalLine(columnWidths);
printRow(headers, columnWidths);
printHorizontalLine(columnWidths);
for (String[] row : data) {
printRow(row, columnWidths);
}
printHorizontalLine(columnWidths);
}
private static void printRow(String[] values, int[] columnWidths) {
System.out.print("|");
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
String value = values[i];
int width = columnWidths[i];
System.out.print(String.format(" %-" + width + "s |", value));
}
System.out.println();
}
private static void printHorizontalLine(int[] columnWidths) {
System.out.print("+");
for (int width : columnWidths) {
System.out.print("-".repeat(width + 2) + "+");
}
System.out.println();
}
private static int[] calculateColumnWidths(String[] headers, String[]... data) {
int columns = headers.length;
int[] columnWidths = new int[columns];
for (String[] row : data) {
for (int i = 0; i < columns; i++) {
int length = row[i].length();
if (length > columnWidths[i]) {
columnWidths[i] = length;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < columns; i++) {
int headerLength = headers[i].length();
if (headerLength > columnWidths[i]) {
columnWidths[i] = headerLength;
}
}
return columnWidths;
}
}
The program begins with the main method, initializing a table with headers and data, and then proceeding to call the printTable method. Within printTable, variable arguments for headers and data are handled, and column widths are calculated using the calculateColumnWidths method.
This method ensures proper formatting by determining the maximum width required for each column based on both headers and data values. The printRow method prints a row, aligning and padding values according to the calculated column widths.
Finally, the printHorizontalLine method adds a line of + and - characters to visually separate rows, contributing to improved table readability.
Output:
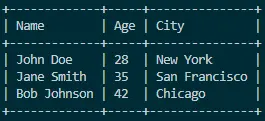
Mastering the art of table printing in Java involves a combination of dynamic formatting, thoughtful column width calculation, and the strategic use of separators. This article presented a comprehensive example, demonstrating how to create visually appealing tables using System.out.print and formatting methods.
Adopting these techniques empowers Java developers to enhance the presentation of data in their applications and command line tools.
Using StringBuilder to Print a Table in Java
Using StringBuilder in Java for table printing is efficient as it allows dynamic construction of the table structure. It enhances performance by minimizing string concatenation, ensures code readability, and facilitates easy customization of tables.
StringBuilder is mutable, making it suitable for building complex and formatted tables with less memory overhead compared to string concatenation.
Let’s dive into a complete working example that demonstrates how to print a visually appealing table in Java using the StringBuilder class. This example will incorporate column and row separators represented by | and -, respectively.
Importantly, the values in the table will be dynamic, avoiding hardcoded entries.
public class TablePrinter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
printTable(new String[] {"Name", "Age", "City"}, new String[] {"John Doe", "28", "New York"},
new String[] {"Jane Smith", "35", "San Francisco"},
new String[] {"Bob Johnson", "42", "Chicago"});
}
private static void printTable(String[] headers, String[]... data) {
StringBuilder table = new StringBuilder();
// Print the header row
printHorizontalLine(table, headers.length);
printRow(table, headers);
printHorizontalLine(table, headers.length);
// Print data rows
for (String[] row : data) {
printRow(table, row);
}
// Print the bottom line
printHorizontalLine(table, headers.length);
System.out.println(table.toString());
}
private static void printRow(StringBuilder table, String[] values) {
table.append("|");
for (String value : values) {
table.append(String.format(" %-15s |", value));
}
table.append("\n");
}
private static void printHorizontalLine(StringBuilder table, int columns) {
table.append("+");
for (int i = 0; i < columns; i++) {
table.append("-".repeat(17) + "+");
}
table.append("\n");
}
}
The program’s entry point is the main method, initiating a table with headers and data before invoking the printTable method. Within printTable, the method handles variable arguments for headers and data, initializing a StringBuilder and calling auxiliary methods to construct the table.
The printRow method appends each value to the StringBuilder, ensuring left-aligned and padded formatting. Similarly, the printHorizontalLine method appends a line of + and - characters to the StringBuilder, providing a visual separation between rows.
Output:
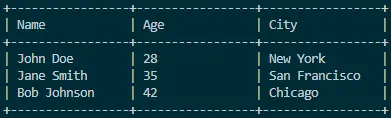
Printing tables in Java using the StringBuilder class provides a clean and efficient way to dynamically construct well-formatted tables. By adopting this approach, developers gain the ability to customize the table structure easily, ensuring a visually appealing presentation of data.
The example presented in this article showcases the power of StringBuilder in simplifying the process of creating beautiful and flexible tables in Java.
Using Formatter to Print a Table in Java
Using Formatter in Java for table printing provides a concise and expressive way to format and construct tables. It simplifies code by handling string formatting, ensures precision, and offers flexibility in creating visually appealing tables.
Formatter also supports localization, making it a versatile choice for tabular data presentation in a clear and organized manner.
Let’s delve into a complete working example that demonstrates how to print a visually appealing table in Java using the Formatter class. This example will incorporate column and row separators represented by | and -, respectively.
Most importantly, the values in the table will be dynamic, avoiding hardcoded entries.
import java.util.Formatter;
public class TablePrinter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
printTable(new String[] {"Name", "Age", "City"}, new String[] {"John Doe", "28", "New York"},
new String[] {"Jane Smith", "35", "San Francisco"},
new String[] {"Bob Johnson", "42", "Chicago"});
}
private static void printTable(String[] headers, String[]... data) {
// Create a StringBuilder to hold the formatted table
StringBuilder table = new StringBuilder();
// Create a Formatter object attached to the StringBuilder
try (Formatter formatter = new Formatter(table)) {
// Print the header row
printHorizontalLine(formatter, headers.length);
printRow(formatter, headers);
printHorizontalLine(formatter, headers.length);
// Print data rows
for (String[] row : data) {
printRow(formatter, row);
}
// Print the bottom line
printHorizontalLine(formatter, headers.length);
}
// Output the formatted table
System.out.println(table.toString());
}
private static void printRow(Formatter formatter, String[] values) {
formatter.format("| %-15s | %-15s | %-15s |\n", values[0], values[1], values[2]);
}
private static void printHorizontalLine(Formatter formatter, int columns) {
formatter.format("+-----------------+-----------------+-----------------+\n");
}
}
The program’s entry point is the main method, responsible for initializing a table with headers and data, followed by the invocation of the printTable method. Within the printTable method, a StringBuilder and a Formatter are created and utilized to format and construct the table through auxiliary methods.
The printRow method employs the Formatter for left-aligned and padded value printing, while the printHorizontalLine method uses the Formatter to append a line of + and - characters, visually separating rows. Ensuring proper resource management, the try-with-resources statement automatically closes the Formatter resource.
Output:
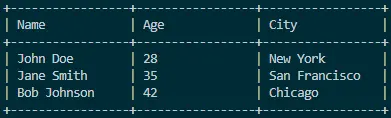
Utilizing the Formatter class in Java for table printing offers a concise and expressive approach, enhancing code readability and maintainability. The example provided in this article demonstrates the simplicity and elegance of crafting well-formatted tables dynamically.
Adopting this technique empowers developers to efficiently present tabular data in a visually appealing manner, a valuable skill in various Java applications.
Using PrintStream to Print a Table in Java
Using PrintStream in Java for table printing offers a straightforward approach, simplifying code and ensuring proper resource management. It provides a convenient way to print formatted output, making it suitable for dynamically constructing visually appealing tables.
PrintStream is particularly useful for command-line applications, facilitating efficient and readable representation of tabular data.
Let’s dive into a complete working example that showcases how to print a beautifully formatted table in Java using the PrintStream class. This example incorporates column and row separators represented by | and -, respectively.
Importantly, the values in the table are dynamic, avoiding hardcoded entries.
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class TablePrinter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (PrintStream out = new PrintStream(System.out)) {
printTable(out, new String[] {"Name", "Age", "City"},
new String[] {"John Doe", "28", "New York"},
new String[] {"Jane Smith", "35", "San Francisco"},
new String[] {"Bob Johnson", "42", "Chicago"});
}
}
private static void printTable(PrintStream out, String[] headers, String[]... data) {
// Print the header row
printHorizontalLine(out, headers.length);
printRow(out, headers);
printHorizontalLine(out, headers.length);
// Print data rows
for (String[] row : data) {
printRow(out, row);
}
// Print the bottom line
printHorizontalLine(out, headers.length);
}
private static void printRow(PrintStream out, String[] values) {
out.print("|");
for (String value : values) {
out.printf(" %-15s |", value);
}
out.println();
}
private static void printHorizontalLine(PrintStream out, int columns) {
out.print("+");
for (int i = 0; i < columns; i++) {
out.print("-".repeat(17) + "+");
}
out.println();
}
}
The main method serves as the program’s entry point, initializing a table with headers and data. Subsequently, it invokes the printTable method within a try-with-resources block, ensuring proper handling of resources.
The printTable method, taking a PrintStream and variable arguments for headers and data, utilizes auxiliary methods to format and construct the table. The printRow method employs PrintStream for left-aligned and padded value printing, while the printHorizontalLine method uses PrintStream to create a visual separation between rows.
The try-with-resources statement guarantees the automatic closure of the PrintStream resource, ensuring effective resource management.
Output:
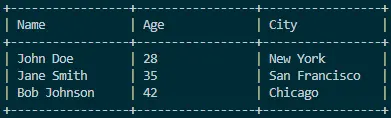
Utilizing the PrintStream class in Java for table printing provides a straightforward and effective way to dynamically construct and print visually appealing tables. The example presented in this article demonstrates the simplicity and elegance of using PrintStream to format tables dynamically.
By adopting this approach, Java developers can enhance the presentation of tabular data in their applications, combining flexibility and aesthetics seamlessly.
Conclusion
Printing tables in Java is essential for presenting data in a structured and readable format. The methods discussed—System.out.print with formatting, StringBuilder, Formatter, and PrintStream—offer various approaches with distinct advantages.
These techniques enhance code readability, enable dynamic customization, and ensure visually appealing presentations. Whether it’s for command-line tools or data analysis applications, choosing the appropriate method depends on specific requirements.
Mastering these methods empowers Java developers to efficiently communicate information, improving the user experience and facilitating informed decision-making.
Rupam Saini is an android developer, who also works sometimes as a web developer., He likes to read books and write about various things.
LinkedIn