How to Print HashMap in Java
-
Importance of Printing
HashMapElements in Java -
Methods on How to Print
HashMapElements in Java - Conclusion
This article explores the significance of printing HashMaps in Java and provides insights into various methods, such as forEach, entrySet, keySet, Stream API, Iterator, values, BiConsumer, and Consumer, offering a comprehensive overview of efficient approaches to handle and display HashMap elements.
HashMap is an implementation class of the Map interface that is used to collect elements into key and value pairs. We can use various methods to print its elements.
Importance of Printing HashMap Elements in Java
Printing HashMap elements in Java is essential for debugging, logging, and understanding program state. It offers quick insights into key-value pairs stored within the HashMap, aiding developers in identifying potential issues or verifying correct data associations.
During development, printing HashMap contents is a common practice to verify the correctness of data input, ensuring that the expected values are stored. Additionally, when troubleshooting or analyzing code, printing HashMap elements facilitates the identification of patterns, duplicates, or unexpected values.
This simple action is a valuable tool for maintaining code quality, enhancing transparency, and accelerating the debugging process in Java applications.
Methods on How to Print HashMap Elements in Java
Using a forEach and Lambda Expression
Using forEach and lambda expressions in Java for printing HashMap elements offers a concise and expressive way to iterate over entries, enhancing code readability. Compared to traditional methods, it reduces boilerplate code, simplifies syntax, and aligns with modern programming paradigms, making the code more elegant and efficient.
Code Example:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class PrintHashMapWithForEach {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a sample HashMap
Map<String, Integer> studentScores = new HashMap<>();
studentScores.put("Alice", 95);
studentScores.put("Bob", 88);
studentScores.put("Charlie", 92);
// Printing HashMap using forEach and lambda expression
System.out.println("Printing HashMap using forEach and lambda expression:");
studentScores.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(key + ": " + value));
}
}
The code starts by importing essential Java packages for HashMap operations. A HashMap named studentScores is then created to hold student names and scores.
Sample data is added to this HashMap. The primary task is achieved using the forEach method coupled with a lambda expression, providing a concise and expressive way to iterate over the HashMap and print each key-value pair.
This approach simplifies code, enhances readability, and aligns with modern Java programming practices.
Output:
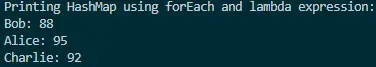
This output demonstrates how the combination of forEach and lambda expression provides a concise and expressive way to print HashMap elements. The code is not only more readable but also aligns with the modern paradigms of Java programming, showcasing the efficiency and elegance of functional programming techniques.
Using the entrySet() Method
entrySet() in Java is crucial for printing HashMap elements as it provides a direct view of key-value pairs. This method simplifies iteration, offering efficiency and clarity.
Compared to alternatives, it minimizes code, improves performance, and aligns with best practices, ensuring straightforward access to both keys and values in a HashMap.
Code Example:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class PrintHashMapWithEntrySet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a sample HashMap
Map<String, Integer> studentScores = new HashMap<>();
studentScores.put("Alice", 95);
studentScores.put("Bob", 88);
studentScores.put("Charlie", 92);
// Printing HashMap using entrySet method
System.out.println("Printing HashMap using entrySet method:");
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : studentScores.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ": " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
The code begins by importing Java packages essential for HashMap operations. A HashMap, named studentScores, is created to store student names and their scores.
Sample data is then added to this HashMap. The primary task is accomplished by using the entrySet() method, providing a set view of HashMap entries.
This set is iterated over using an enhanced for loop, enabling the printing of each key-value pair. This approach ensures clarity and simplicity in code, aligning with best practices for working with HashMaps in Java.
Output:
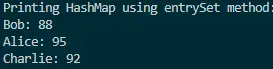
This output illustrates how the entrySet() method, in conjunction with an enhanced for loop, provides an effective and readable way to print the contents of a HashMap. It offers a straightforward approach for developers to examine the key-value pairs stored in the HashMap, enhancing code clarity and simplifying debugging tasks.
Using the keySet() Method
Using keySet() in Java for printing HashMap elements simplifies code by directly accessing keys. This method enhances readability, reduces complexity, and ensures efficient key-based iteration.
Compared to alternative approaches, it offers a clear and concise way to work with keys in a HashMap, improving code quality.
Code Example:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class PrintHashMapWithKeySet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a sample HashMap
Map<String, Integer> studentScores = new HashMap<>();
studentScores.put("Alice", 95);
studentScores.put("Bob", 88);
studentScores.put("Charlie", 92);
// Printing HashMap using keySet method
System.out.println("Printing HashMap using keySet method:");
for (String key : studentScores.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key + ": " + studentScores.get(key));
}
}
}
The code starts by importing Java packages essential for HashMap operations. A HashMap named studentScores is then created to store student names and their corresponding scores.
Sample data is added to this HashMap. To print the HashMap elements, the keySet() method is used to obtain a set view of the keys.
These keys are then iterated over using an enhanced for loop, allowing each key-value pair to be printed. This method provides a clear and concise approach for iterating through keys and accessing associated values in a HashMap.
Output:
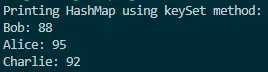
This output demonstrates how the keySet() method, in combination with an enhanced for loop, provides an efficient and readable way to print the contents of a HashMap. By accessing the values using the keys, this approach ensures clarity and simplicity in code, making it a valuable tool for developers working with HashMaps in Java.
Using the Java 8 Stream API
Java 8 Stream API simplifies printing HashMap elements with a concise and functional approach. It enhances code readability, reduces boilerplate, and aligns with modern programming paradigms.
Compared to traditional methods, it offers a more expressive and efficient way to handle collections, making the code more elegant and concise.
Code Example:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class PrintHashMapWithStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a sample HashMap
Map<String, Integer> studentScores = new HashMap<>();
studentScores.put("Alice", 95);
studentScores.put("Bob", 88);
studentScores.put("Charlie", 92);
// Printing HashMap using Stream API
System.out.println("Printing HashMap using Stream API:");
studentScores.entrySet().stream().forEach(
entry -> System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ": " + entry.getValue()));
}
}
The code commences by importing crucial Java packages for HashMap operations. Subsequently, a HashMap named studentScores is established to store student names and their associated scores.
Sample data is then incorporated into this HashMap. The primary objective of printing HashMap elements is accomplished by leveraging the Stream API on the entrySet().
This approach facilitates a streamlined iteration over the elements and executes the operation of printing each key-value pair. This method aligns with modern programming practices, providing a concise and expressive solution for HashMap processing in Java.
Output:
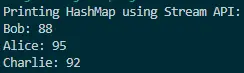
This output showcases how the Java 8 Stream API simplifies the process of printing HashMap elements. The code is more expressive and declarative, aligning with the modern functional programming paradigm.
The Stream API enhances readability and reduces boilerplate, making it a valuable tool for developers working on Java projects.
Using an Iterator
Using an iterator in Java for printing HashMap elements provides a classic and versatile approach. It allows controlled traversal, improving memory efficiency and supporting bidirectional movement.
Compared to other methods, iterators offer fine-grained control over the iteration process, making them valuable for scenarios where precise navigation or manipulation of HashMap entries is required. While it may not be as concise as some newer approaches, understanding how to use an Iterator is fundamental for any Java developer and contributes to a deeper understanding of the language.
Code Example:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
public class PrintHashMapWithIterator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a sample HashMap
Map<String, Integer> studentScores = new HashMap<>();
studentScores.put("Alice", 95);
studentScores.put("Bob", 88);
studentScores.put("Charlie", 92);
// Printing HashMap using Iterator
System.out.println("Printing HashMap using Iterator:");
// Obtaining an iterator for the entry set
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> iterator = studentScores.entrySet().iterator();
// Iterating through the entries and printing them
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry = iterator.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ": " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
The code begins by importing essential Java packages for HashMaps and Iterator. Following that, a HashMap named studentScores is created to store student names and their corresponding scores.
Sample data is then added to populate this HashMap. To print the elements of the HashMap, an Iterator is employed.
It traverses through the entry set of the HashMap, and for each iteration, the associated entry is printed. This method allows controlled traversal through the HashMap’s entries, providing a classic and versatile approach for processing key-value pairs in Java.
Output:
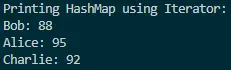
This output demonstrates how the Iterator method provides a reliable and flexible way to traverse through a HashMap’s entries, making it a valuable technique for various scenarios. While it might involve more lines of code compared to some newer approaches, understanding the underlying concepts of iteration is crucial for a comprehensive grasp of Java programming.
Using the values() Method
Utilizing values() in Java for printing HashMap elements simplifies code by directly accessing the collection of values. This method enhances clarity, reduces complexity, and ensures efficient iteration over values.
Compared to alternative approaches, it provides a straightforward way to work specifically with the values in a HashMap, contributing to cleaner and more readable code.
Consider the following Java code snippet:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class PrintHashMapWithValues {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a sample HashMap
Map<String, Integer> studentScores = new HashMap<>();
studentScores.put("Alice", 95);
studentScores.put("Bob", 88);
studentScores.put("Charlie", 92);
// Printing HashMap values using values() method
System.out.println("Printing HashMap values using values() method:");
// Obtaining the values collection
for (Integer score : studentScores.values()) {
System.out.println("Score: " + score);
}
}
}
The code first imports essential Java packages for HashMaps. Then, it declares and initializes a HashMap named studentScores to store student names and scores.
Sample data is added to populate this HashMap. To print the values of the HashMap, the values() method is used.
This method retrieves a collection view of the values, and an enhanced for loop iterates over this collection, allowing each value to be printed. This approach simplifies the code, providing a concise way to work specifically with the values in a HashMap in Java.
Output:
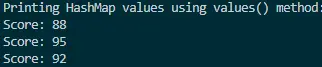
This output demonstrates how the values() method simplifies the process of printing the values stored in a HashMap. By directly obtaining a collection view, developers can easily iterate through the values, providing a concise and effective solution for scenarios where printing or processing the values is the primary objective.
Using the BiConsumer Interface
Using BiConsumer in Java for printing HashMap elements enables custom actions on key-value pairs, enhancing flexibility and code expressiveness. This method simplifies iteration, reducing code redundancy and aligning with a functional programming paradigm.
This interface is particularly useful when you want to customize the behavior of processing each entry. This approach allows developers to apply their logic to each key-value pair, providing a more tailored solution for specific requirements.
Compared to other approaches, it offers a concise and powerful mechanism to define specific behavior for processing each entry in a HashMap.
Code Example:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;
public class PrintHashMapWithBiConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a sample HashMap
Map<String, Integer> studentScores = new HashMap<>();
studentScores.put("Alice", 95);
studentScores.put("Bob", 88);
studentScores.put("Charlie", 92);
// Printing HashMap using BiConsumer
System.out.println("Printing HashMap using BiConsumer:");
// Defining a BiConsumer to print key-value pairs
BiConsumer<String, Integer> printKeyValue =
(key, value) -> System.out.println(key + ": " + value);
// Applying the BiConsumer to each entry in the HashMap
studentScores.forEach(printKeyValue);
}
}
The code begins by importing necessary Java packages for HashMaps and the BiConsumer interface. It then declares and initializes a HashMap named studentScores to store student names and scores, with sample data added.
To print the HashMap elements, a BiConsumer is defined to print key-value pairs. The forEach method is employed to apply this BiConsumer to each entry in the HashMap, providing a concise and expressive way to customize the processing of key-value pairs in Java.
Output:
![]()
This output demonstrates how the BiConsumer method allows for a more customized approach to printing HashMap elements. It provides a mechanism for developers to define their logic for processing each key-value pair, making it a versatile tool for scenarios where a more tailored action is required.
Using Consumer and entrySet()
Using Consumer and entrySet() in Java for printing HashMap elements provides a customizable and direct approach. It simplifies code, offering clarity and expressiveness.
The entrySet() method returns a set view of the entries, and when combined with a Consumer, it allows you to define the action to be taken on each entry. Compared to other methods, it minimizes boilerplate, allows tailored actions on each entry, and aligns with modern programming practices, making it an efficient choice for iterating over and processing HashMap entries.
Code Example:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
public class PrintHashMapWithConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a sample HashMap
Map<String, Integer> studentScores = new HashMap<>();
studentScores.put("Alice", 95);
studentScores.put("Bob", 88);
studentScores.put("Charlie", 92);
// Printing HashMap using Consumer and entrySet()
System.out.println("Printing HashMap using Consumer and entrySet():");
// Defining a Consumer to print key-value pairs
Consumer<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> printEntry =
entry -> System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ": " + entry.getValue());
// Applying the Consumer to the entry set of the HashMap
studentScores.entrySet().forEach(printEntry);
}
}
The code imports necessary Java packages for HashMaps and the Consumer interface. It declares and initializes a HashMap named studentScores to store student names and scores, with sample data added.
To print the HashMap elements, a Consumer is defined to print key-value pairs. The entrySet() method is employed to obtain a set view of the entries, and the forEach method applies the Consumer to each entry.
This method ensures a direct and customizable approach for iterating over and processing HashMap entries in Java.
Output:
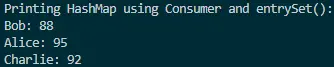
This output demonstrates how the combination of Consumer and entrySet() provides a flexible and concise way to print the elements of a HashMap. The Consumer interface allows developers to define their logic for processing each entry, offering a customizable approach to working with HashMaps.
Conclusion
Printing HashMaps is a fundamental aspect of Java programming, providing insights into stored data. The discussed methods, including forEach with lambda expressions, entrySet, keySet, Stream API, Iterator, values, BiConsumer, and Consumer, offer diverse approaches to achieve this task.
These methods address specific needs, allowing developers to choose the most suitable option based on their requirements. Whether prioritizing simplicity, customization, or modern coding paradigms, the versatility of these methods empowers Java developers to handle HashMaps efficiently, ensuring clarity, readability, and adaptability in their code.