Fix Java.Lang.NoClassDefFoundError: Could Not Initialize Class Error
-
Possible Causes and Solutions for the
Java.Lang.NoClassDefFoundError: Could Not Initialize ClassError - Conclusion
This article examines potential causes of the java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: Could not initialize class error in Java and provides a practical example demonstrating an effective method for its prevention.
Possible Causes and Solutions for the Java.Lang.NoClassDefFoundError: Could Not Initialize Class Error
java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError occurs when the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) or the ClassLoader is unable to find or load a particular class at runtime. This error can happen for various reasons, and the causes and solutions may vary.
Here are some common causes and their solutions:
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
Classpath Issues |
The required class is not in the classpath. |
Ensure that the JAR file containing the class is included in the classpath. Set the classpath using the -cp option or update the CLASSPATH environment variable. |
| Class Loading Order | Classes are loaded in a different order than expected. | Check the class loading order. Ensure that the class is loaded before it is used. Resolve dependencies to load the classes in the correct order. |
| Incorrect Package or Class Name | The package or class name in the code does not match the actual structure. | Verify the package and class names in the code. Ensure they match the actual structure of your project. |
| Missing JAR Files | Required JAR files are missing or not accessible. | Ensure that all necessary JAR files are present and accessible by the JVM. |
| Dependency Issues | Conflicts or version mismatches between different versions of libraries. | Resolve dependency issues by using compatible versions of libraries. Tools like Maven or Gradle can help manage dependencies efficiently. |
| Static Initialization Failure | An exception occurred during the static initialization of a class. | Check the static initialization block of the class for any exceptions. Handle them appropriately and ensure that the class is initialized correctly. |
ClassLoader Issues |
Issues with custom ClassLoaders or dynamic loading of classes. |
Review any custom ClassLoader code and ensure that it correctly loads and initializes classes. |
| Java Version Mismatch | Running code compiled with a higher Java version on a lower version. | Compile the code with a version compatible with the target JVM or update the JVM to a higher version. |
| Memory Issues | Running out of memory while loading classes. | Increase the JVM memory settings using the -Xmx and -Xms options. |
| Corrupted JAR Files | JAR files containing the classes are corrupted. | Verify the integrity of the JAR files. If they are corrupted, replace them with a valid copy. |
Investigating and addressing the specific cause of the NoClassDefFoundError is crucial for resolving the issue. Analyzing the error message, reviewing the code, and understanding the application’s class-loading mechanism can help in identifying the root cause and applying an appropriate solution.
In this article, we’ll focus on addressing the most common causes and solutions for the Java.Lang.NoClassDefFoundError: Could Not Initialize Class error. This error often occurs due to issues with class loading, package or class name mismatches, classpath problems, and other related issues.
Fixing Error Caused by Classpath Issues
The java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: Could not initialize class error is a common issue encountered by Java developers, often caused by classpath problems. Classpath issues arise when the JVM cannot locate the required class files at runtime, leading to errors during class loading and initialization.
Consider a scenario where a Java application encounters the NoClassDefFoundError due to classpath misconfiguration. Let’s walk through a correct and functional code example that effectively addresses classpath issues to prevent this error.
public class ClasspathExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GreetingService greetingService = new GreetingService();
System.out.println(greetingService.getGreeting());
}
}
class GreetingService {
public String getGreeting() {
return "Hello, Java Specialist!";
}
}
In this code example, we have a Java program with two classes: ClasspathExample and GreetingService. The ClasspathExample class contains the main method, which is the starting point of the program.
Within the main method, we instantiate the GreetingService class and call its getGreeting() method to retrieve a predefined greeting message. The GreetingService class itself provides the getGreeting() method, which returns the hardcoded greeting message.
In order to run the program successfully, both classes must be compiled properly and included in the classpath. After compiling the classes using the javac command, the ClasspathExample class can be executed using the java command.
Upon successful execution, the program will print the greeting message to the console.
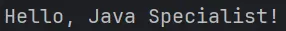
By correctly setting up the classpath and ensuring that all required classes are accessible to the JVM, we’ve effectively prevented the java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError. This example demonstrates the importance of proper classpath configuration in Java applications, ensuring that all dependencies are resolved at runtime, thus enabling smooth execution without encountering class loading errors.
Fixing Error Caused by Class Loading Order
This error often stems from issues related to class loading order, where a class is attempted to be initialized before its dependencies are properly loaded. Understanding and managing class loading orders is crucial for ensuring the smooth execution of Java applications.
Consider a scenario where a Java application encounters the NoClassDefFoundError due to an incorrect class loading order. Let’s examine a correct and functional code example that effectively resolves this issue.
public class ClassLoadingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
initialize();
System.out.println("Main method execution completed.");
}
private static void initialize() {
DependencyClass.doSomething();
}
}
class DependencyClass {
static {
System.out.println("Static initialization of DependencyClass.");
}
public static void doSomething() {
System.out.println("DependencyClass doing something.");
}
}
In this Java program, we have two classes: ClassLoadingExample and DependencyClass. The ClassLoadingExample class serves as the entry point with its main method, where it calls the initialize() method.
This initialize() method triggers an operation in the DependencyClass. The DependencyClass contains a static initialization block, executed upon class loading, along with a doSomething() method for a specific action.
When running the code, it’s crucial to understand the sequence of class loading and initialization. The JVM first loads ClassLoadingExample, encountering the initialize() call, which in turn loads DependencyClass.
The static block in DependencyClass initializes before any method calls, thus preventing the NoClassDefFoundError. The program then executes the doSomething() method and completes the main method.
Upon running the program, the output should demonstrate the successful execution of the initialize() method, followed by the completion message from the main method:
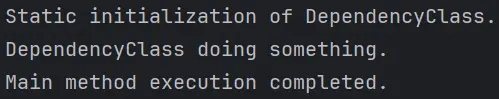
This output confirms that the class loading order is properly managed, mitigating the risk of encountering NoClassDefFoundError.
By understanding and managing the class loading order in Java applications, we can effectively prevent the occurrence of java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError. This example illustrates the importance of ensuring that dependencies are loaded and initialized in the correct sequence to maintain the integrity and functionality of Java programs.
Fixing Error Caused by Incorrect Package or Class Name
In Java development, the java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: Could not initialize class error can be a stumbling block for developers, often arising from incorrect package or class names in the code. Ensuring accurate package and class naming is fundamental to the structure and functionality of Java applications.
Imagine a scenario where a Java application encounters the NoClassDefFoundError due to mismatches in package or class names. Let’s delve into a correct and functional code example that effectively resolves this issue.
package com.example;
public class CorrectPackageNameExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GreetingService greetingService = new GreetingService();
System.out.println(greetingService.getGreeting());
}
}
class GreetingService {
public String getGreeting() {
return "Hello, Java Specialist!";
}
}
In this Java code, we find a class named CorrectPackageNameExample within the package com.example. Additionally, the file includes a GreetingService class.
The CorrectPackageNameExample class contains the main method, which is the starting point of the program. Inside main, we instantiate the GreetingService class and call its getGreeting() method to retrieve a predefined greeting message.
In order to compile and run the code successfully, it’s crucial to ensure that the package and class names match the directory structure and file names. After compiling the code using the javac command, execute the CorrectPackageNameExample class to observe the program’s behavior.
Upon running the program, the output should display the greeting message:
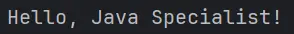
This output confirms that the package and class names are correctly aligned, mitigating the risk of encountering NoClassDefFoundError due to incorrect package or class names.
By ensuring accurate package and class naming conventions, we can effectively prevent the occurrence of java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError. This example underscores the importance of maintaining consistency between package declarations, class definitions, and directory structures in Java applications.
Conclusion
This article has addressed the common runtime error in Java, specifically the java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: Could not initialize class error. We explored potential causes for this issue and provided some straightforward examples to demonstrate its prevention.
By showcasing a well-structured Java class with a static initialization block and careful consideration of initialization logic, developers can avoid encountering this error. The key takeaway is that a thoughtful approach to class design and initialization processes contributes to the creation of robust Java applications, minimizing the risk of runtime errors during class loading.
Related Article - Java Error
- How to Fix the Error: Failed to Create the Java Virtual Machine
- How to Fix the Missing Server JVM Error in Java
- How to Fix the 'No Java Virtual Machine Was Found' Error in Eclipse
- How to Fix Javax.Net.SSL.SSLHandShakeException: Remote Host Closed Connection During Handshake
- How to Fix the Error: Failed to Create the Java Virtual Machine
- How to Fix Java.Lang.VerifyError: Bad Type on Operand Stack
