How to Solve the Can Only Iterate Over an Array or an Instance of Java.Lang.Iterable Error in Java
-
What Is the Java Error:
Can Only Iterate Over an Array or an Instance of java.lang.iterable -
Solve the
Can Only Iterate Over an Array or an Instance of java.lang.iterableError UsingIterator() -
Convert Collection to Array to Fix the Error Message
Can Only Iterate Over an Array or an Instance of java.lang.iterablein Java -
Use Java Streams to Solve the Error
Can Only Iterate Over an Array or an Instance of java.lang.iterablein Java - Conclusion

Java developers often encounter the error "Can Only Iterate Over an Array or an Instance of Java.Lang.Iterable" when working with collections or data structures. This error indicates a mismatch in the type of object being used in an iteration loop.
In this article, we will explore various methods to solve this error, providing detailed examples and explanations for each approach. We will see why this error occurs and the solution to it.
What Is the Java Error: Can Only Iterate Over an Array or an Instance of java.lang.iterable
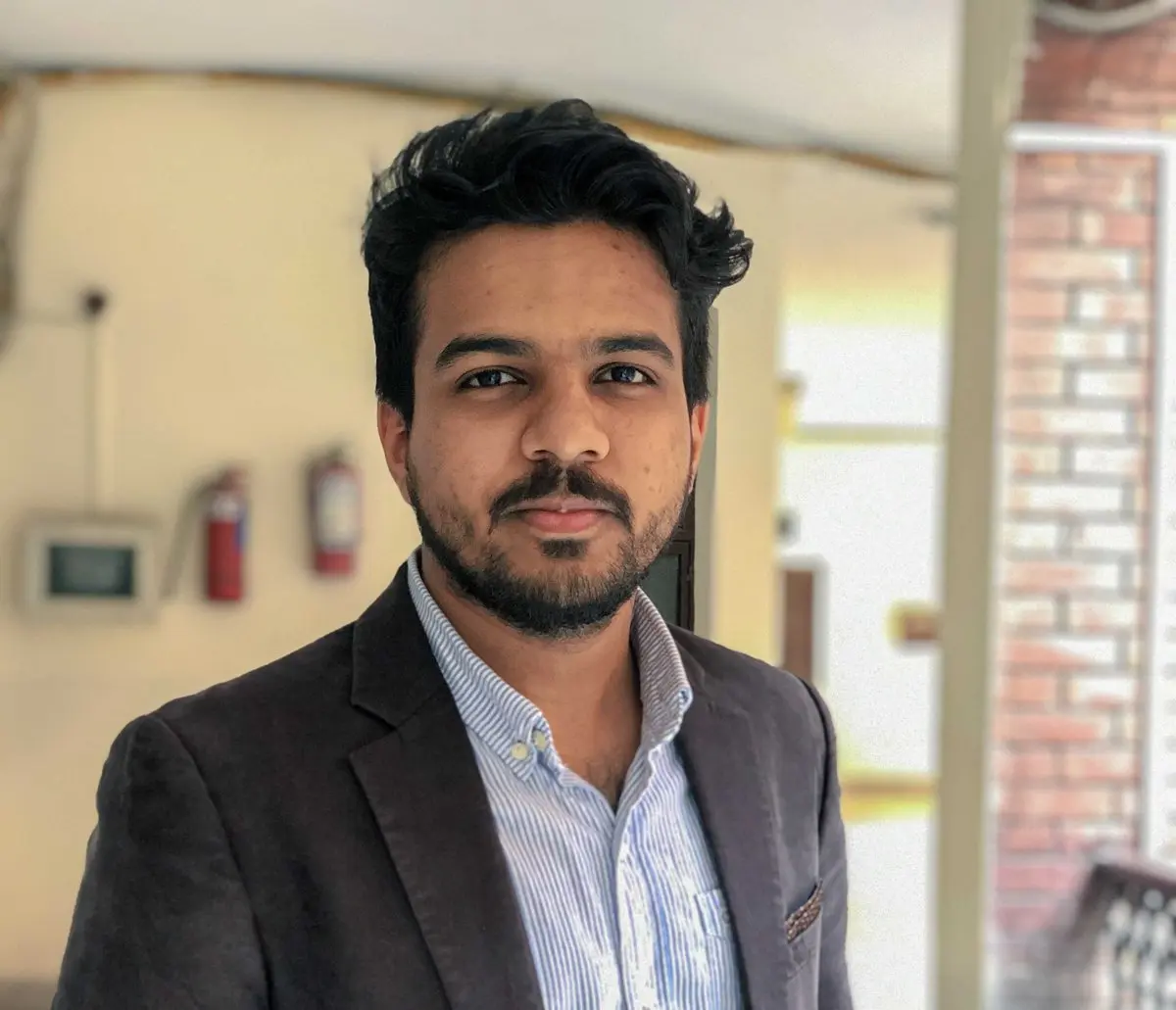
This error is a compile time error, and it’s just as it says. It occurs when there is a problem with the iteration of an array or an instance.
While programming, the user tries to make things easier for themselves, and while doing so, the user uses loops. However, using loops is not always the correct answer.
The error can only iterate over an array or an instance of java.lang.iterable doesn’t mean that it stops the user from using a loop on an array or an instance. It means that a loop is used that doesn’t complement its conditions - for example, the for or foreach loop.
The image below shows how we can encounter this error message in our Java code.
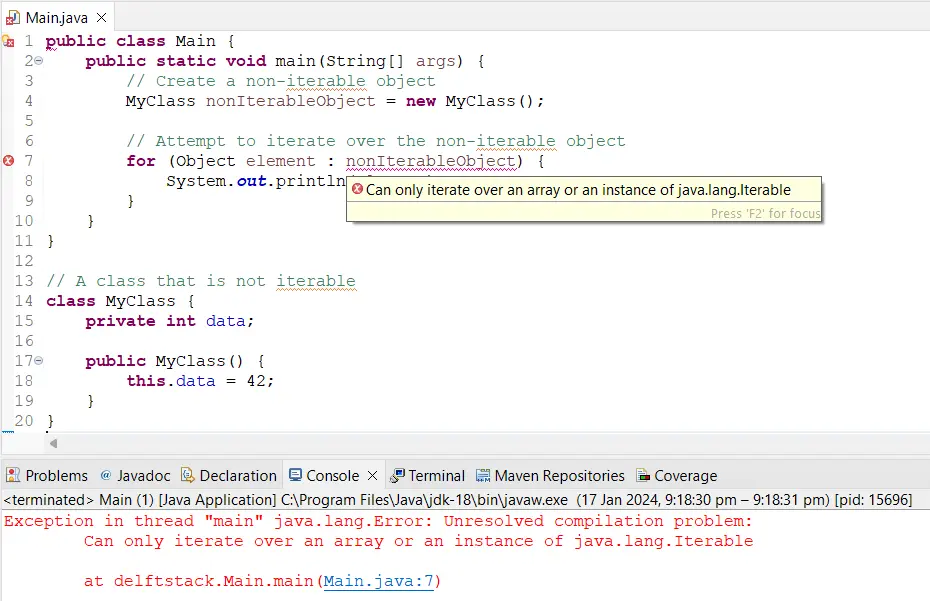
Solve the Can Only Iterate Over an Array or an Instance of java.lang.iterable Error Using Iterator()
In the case of loops, if a foreach loop is used, we have to explicitly type our iterations as sometimes foreach can cause this error to occur. We can do that by using Iterator.
Another way is to use a simple for or while loop.
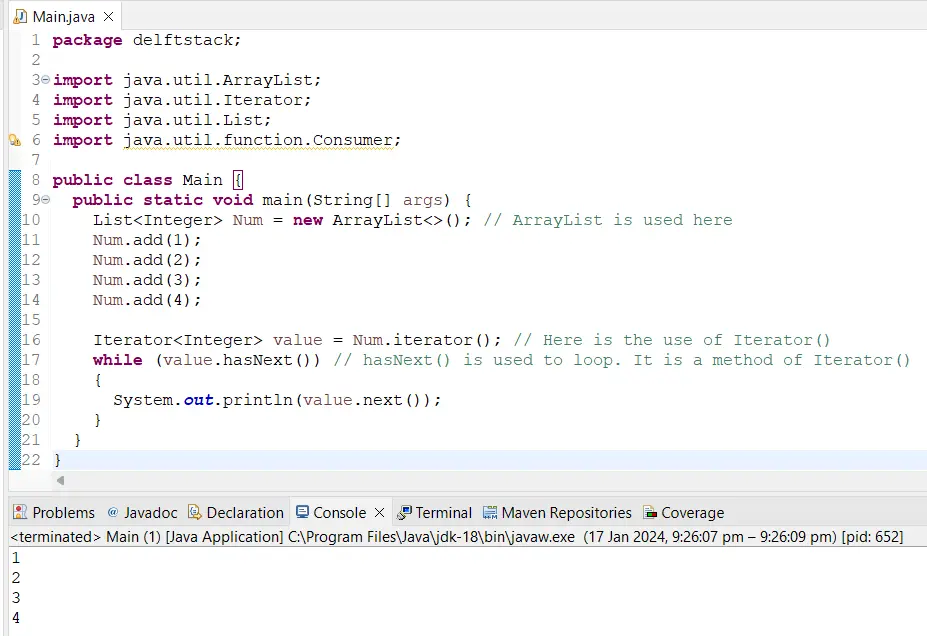
In the code below, we are explicitly iterating an array using an Iterator with a while loop. Here, we will use ArrayList to demonstrate Iterator(). An ArrayList is used here because Iterator() is a method of the ArrayList class.
A while loop is used here to make things easier. This is because while using other loops, for example, for and foreach, the Iterator() method does not work correctly.
Since Iterator() is part of a collection method, it works properly with specific loops, like the while loop.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> Num = new ArrayList<>(); // ArrayList is used here
Num.add(1);
Num.add(2);
Num.add(3);
Num.add(4);
Iterator<Integer> value = Num.iterator(); // Here is the use of Iterator()
while (value.hasNext()) // hasNext() is used to loop. It is a method of Iterator()
{
System.out.println(value.next());
}
}
}
When we execute this code, we get the following output:
Using an Explicit Iterator
Another way to address this issue is by using an explicit iterator, which allows you to iterate over any collection that implements the Iterable interface. Here’s a code example:
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class ExplicitIteratorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> stringList = List.of("Java", "is", "awesome");
// Using explicit iterator
Iterator<String> iterator = stringList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String element = iterator.next();
System.out.println(element);
}
}
}
Output:
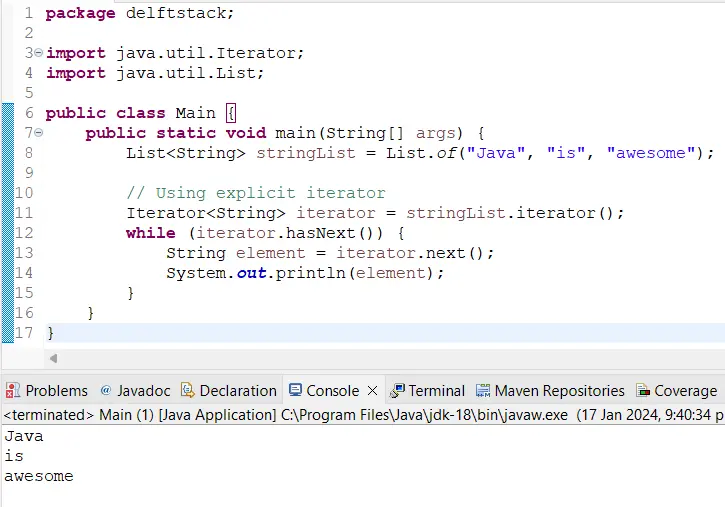
We create an iterator using the iterator() method provided by the List interface. The while loop checks if there are more elements using hasNext() and retrieves the next element with next().
Convert Collection to Array to Fix the Error Message Can Only Iterate Over an Array or an Instance of java.lang.iterable in Java
Another approach is to convert the collection to an array using the toArray() method. This method allows for easy iteration without encountering the mentioned error.
import java.util.List;
public class CollectionToArrayExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> stringList = List.of("Java", "is", "awesome");
// Convert collection to array
String[] stringArray = stringList.toArray(new String[0]);
// Iterate over the array
for (String element : stringArray) {
System.out.println(element);
}
}
}
Output:
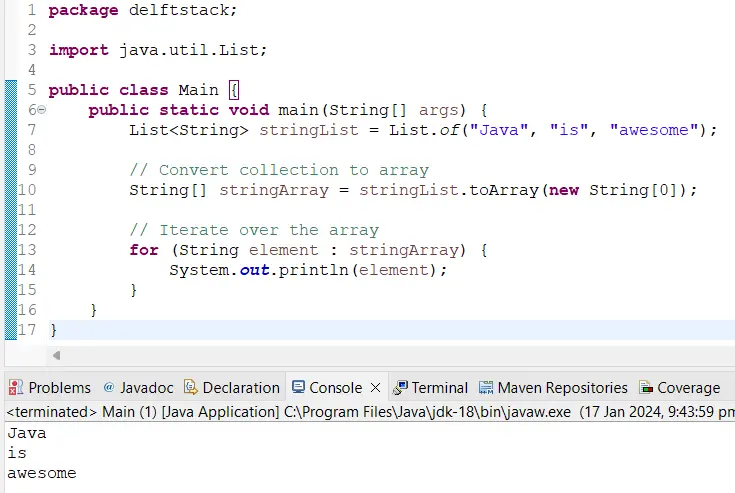
The toArray() method is used to convert the List to an array. We can then iterate over the array using an enhanced for loop.
Use Java Streams to Solve the Error Can Only Iterate Over an Array or an Instance of java.lang.iterable in Java
Java Streams provide a concise and expressive way to process collections. By using the stream() method and various stream operations, we can iterate over elements without encountering the error.
import java.util.List;
public class JavaStreamsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> stringList = List.of("Java", "is", "awesome");
// Using Java Streams
stringList.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
Output:
The stream() method is called on the List, creating a stream of elements. The forEach() method is used to iterate over the elements and perform an action.
Conclusion
In this article, we addressed the common Java error "Can Only Iterate Over an Array or an Instance of Java.Lang.Iterable".
This compile-time error arises from mismatches in object types during iteration loops. We explored the error’s origin and presented three effective methods for resolution.
The article began by explaining the error’s cause, emphasizing the importance of using loops that align with collection conditions. Three key methods were then detailed:
- Using an Explicit Iterator: Demonstrated employing an explicit iterator for seamless iteration over any
Iterablecollection. - Converting Collection to Array: Illustrated using the
toArray()method to convert a collection to an array, bypassing the iteration error. - Using Java Streams: Highlighted Java Streams as an expressive method for processing collections without encountering iteration errors.
In conclusion, developers have diverse tools to resolve the "Can Only Iterate Over an Array or an Instance of Java.Lang.Iterable" error. By selecting the appropriate method based on code requirements, developers can enhance Java application reliability and efficiency.
Haider specializes in technical writing. He has a solid background in computer science that allows him to create engaging, original, and compelling technical tutorials. In his free time, he enjoys adding new skills to his repertoire and watching Netflix.
LinkedInRelated Article - Java Error
- How to Fix the Error: Failed to Create the Java Virtual Machine
- How to Fix the Missing Server JVM Error in Java
- How to Fix the 'No Java Virtual Machine Was Found' Error in Eclipse
- How to Fix Javax.Net.SSL.SSLHandShakeException: Remote Host Closed Connection During Handshake
- How to Fix the Error: Failed to Create the Java Virtual Machine
- How to Fix Java.Lang.VerifyError: Bad Type on Operand Stack
