Linked List Reversal
- Linked List Reversal Algorithm
- Linked List Reversal Illustration
- Linked List Reversal Implementation
- Linked List Reversal Algorithm Complexity
A linked list is a linear data structure. A node of the linked list consists of:
- A data item.
- An address of the next node.
class Node {
int data;
Node *next;
};
This article will introduce how to reverse a linked list given the pointer to the head node of the linked list.
Linked List Reversal Algorithm
Let the head be the first node of the linked list.
Iterative Algorithm
-
Initialize 3 pointers -
currashead,prevandnextasNULL. -
Traverse the linked list until you reach the last node i.e.
curr!=NULLand do the following:- Set
nextascurr->nextto movenextto its next node. - Reverse current node’s direction by pointing them toward
prev. So, setcurr->nextasprev - Set
prevascurrto move it one position ahead. - Set
currasnextto move it one position ahead.
- Set
Recursive Algorithm
-
Divide the list into two parts: the first node, i.e., the
headnode, and the rest of the linked list. -
Call
reverse(head->next), i.e., reverse the rest of the linked list and store the reversed linked list asrev. -
Append
headto the end of the reversed linked listrev. -
Point
headi.e. the tail of the reversed link list toNULL.
Reverse Linked List Using Stack
-
Initialize pointer
currto theheadof the linked list. -
Traverse the linked list and insert each node in the stack one by one.
-
Update
headto the last node in the linked list i.e. the first node in the stack. -
Start popping the nodes out of the stack one by one and append it to the end of reversed linked list.
-
Update the next pointer of the last node to
NULL.
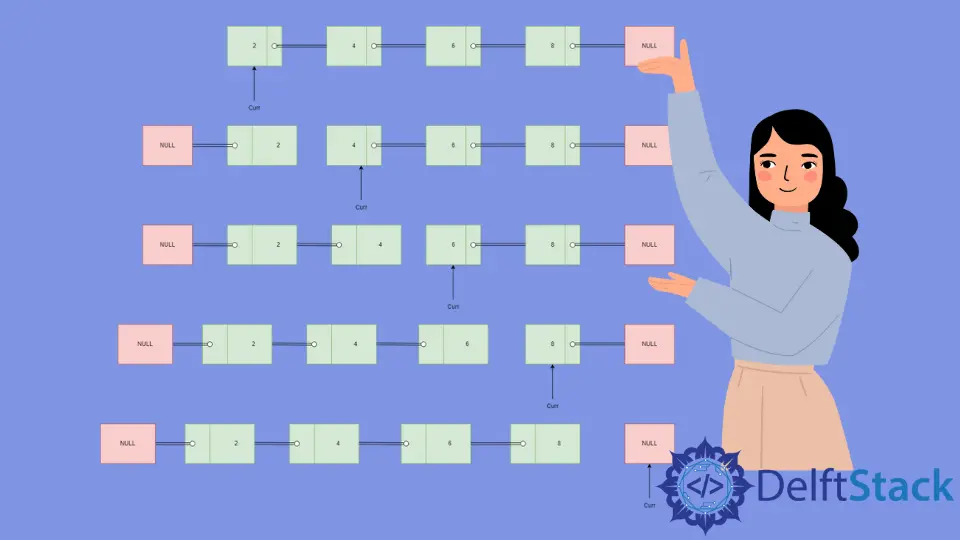
Linked List Reversal Illustration
-
Initialize
currto point towards head i.e. node with data2andprevandcurrasNULL. -
Point
nexttocurr->nextwith a value equal to4. -
Set
curr->nextasprevto get a reversed linked list with2as the head. -
Move
prevtocurri.e. node with data as2andcurrtonexti.e. node with data as4. -
Point
nexttocurr->nextwith a value equal to6. -
Set
curr->nextasprevto get a reversed linked list with2and4as reversed nodes with4as the head. -
Move
prevtocurri.e. node with data as4andcurrtonexti.e. node with data as6. -
Point
nexttocurr->nextwith a value equal to8. -
Set
curr->nextasprevto get a reversed linked list with2,4, and6as reversed nodes with6as the head. -
Move
prevtocurri.e. node with data as6andcurrtonexti.e. node with data as8. -
Point
nexttocurr->nextwhich isNULL. -
Set
curr->nextasprevto get a reversed linked list with2,4,6, and8as reversed nodes with8as the head. -
Move
prevtocurri.e. node with data as8andcurrtoNULLand the algorithm terminates.
Linked List Reversal Implementation
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
Node(int x) {
this->data = x;
this->next = NULL;
}
};
void printList(Node* head) {
Node* curr = head;
while (curr != NULL) {
cout << curr->data << " ";
curr = curr->next;
}
}
Node* reverse(Node* head) {
Node* curr = head;
Node *prev = NULL, *next = NULL;
while (curr != NULL) {
next = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
head = prev;
return head;
}
Node* recursiveReverse(Node* head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head;
Node* rest = recursiveReverse(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return rest;
}
void reverseLL(Node** head) {
stack<Node*> s;
Node* temp = *head;
while (temp->next != NULL) {
s.push(temp);
temp = temp->next;
}
*head = temp;
while (!s.empty()) {
temp->next = s.top();
s.pop();
temp = temp->next;
}
temp->next = NULL;
}
int main() {
Node* head = new Node(1);
head->next = new Node(2);
head->next->next = new Node(3);
head->next->next->next = new Node(4);
head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5);
head->next->next->next->next->next = new Node(6);
head = reverse(head);
printList(head);
cout << "\n";
head = recursiveReverse(head);
printList(head);
cout << "\n";
reverseLL(&head);
printList(head);
cout << "\n";
return 0;
}
Linked List Reversal Algorithm Complexity
Time Complexity
- Average Case
To reverse the complete linked list, we have to visit every node and then append it to reversed list. So, if a linked list has n nodes, the average-case time complexity of traversal is of the order of O(n). The time complexity is of the order of O(n).
- Best Case
The best-case time complexity is O(n). It is the same as average-case time complexity.
- Worst Case
The worst-case time complexity is O(n). It is the same as best-case time complexity.
Space Complexity
This traversal algorithm’s space complexity is O(1) as no extra space other than for temporary pointers is required.
Harshit Jindal has done his Bachelors in Computer Science Engineering(2021) from DTU. He has always been a problem solver and now turned that into his profession. Currently working at M365 Cloud Security team(Torus) on Cloud Security Services and Datacenter Buildout Automation.
LinkedInRelated Article - Data Structure
- Circular Doubly Linked List
- Circular Linked List
- Doubly Linked List
- Linked List Deletion
- Linked List Insertion
- Linked List Merge Sort


