How to Change the Key in a Dictionary in Python
- Assign a New Key and Delete the Old Key in a Dictionary in Python
-
Use the
pop()Function in Python -
Traverse Through the Dictionary Using a
forLoop and Change the Key in a Dictionary in Python - Rebuild an Entirely New Instance in Python
-
Use the
OrderedDictClass in Python -
Use the
Pandas.DataFrameFunction in Python - Conclusion

Dictionaries stand out as one of the most versatile and widely used data structures. They store data in key-value pairs, providing fast access and efficient storage.
However, a common challenge that arises is the need to change the keys of a dictionary. This article introduces various methods to change the key in a dictionary in Python.
Assign a New Key and Delete the Old Key in a Dictionary in Python
While dictionaries are known for their fast access and efficient storage, there may be occasions when you need to alter the keys in a dictionary. One common method for changing a key is using the del statement, which stands for delete.
The following code illustrates this method.
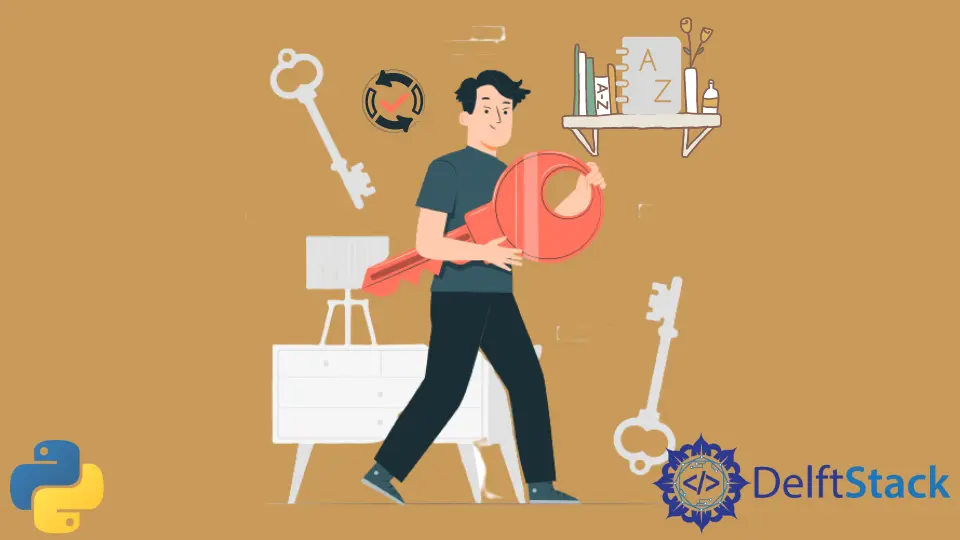
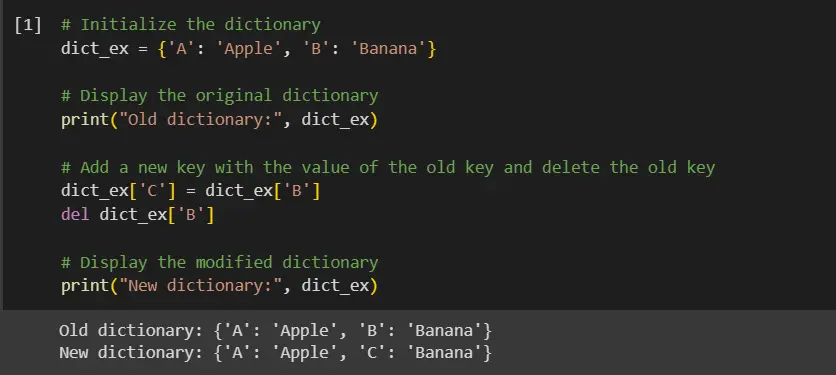
# Initialize the dictionary
dict_ex = {"A": "Apple", "B": "Banana"}
# Display the original dictionary
print("Old dictionary:", dict_ex)
# Add a new key with the value of the old key and delete the old key
dict_ex["C"] = dict_ex["B"]
del dict_ex["B"]
# Display the modified dictionary
print("New dictionary:", dict_ex)
In our code example, we start by initializing the dictionary dict_ex with two key-value pairs. We then print the original dictionary to provide a clear view of its initial state.
Moving on to the modification, we create a new key, C, and assign it the value of the existing key, B, using dict_ex['C'] = dict_ex['B']. Subsequently, we use the del statement to remove the old key B and its associated value from the dictionary.
Finally, we print the modified dictionary to demonstrate the successful replacement of the key B with C.
Output:
Use the pop() Function in Python
Sometimes, it becomes necessary to change a key in a dictionary, which is not directly possible since keys are immutable.
However, we can achieve this by creating a new key and deleting the old one. One efficient way to perform this operation is by using the pop method.
To change the key in a dictionary in Python, refer to the following steps.
-
Pop the old key using the
popfunction. Follow this example.pop(old_key)
-
Assign a new key to the popped old key. Follow this example.
my_dict[new_key] = my_dict.pop(old_key)
The example below illustrates this.
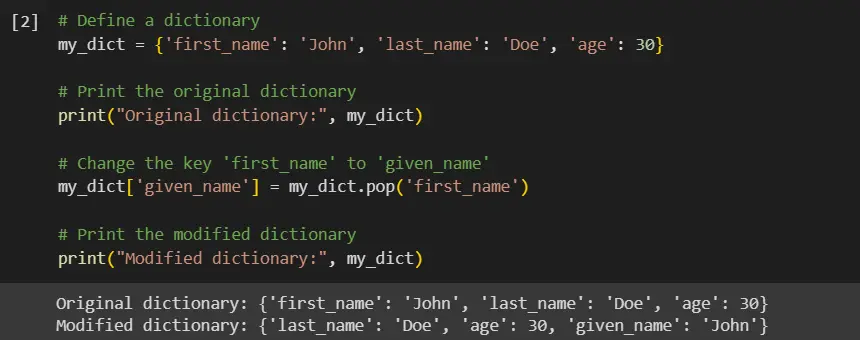
# Define a dictionary
my_dict = {"first_name": "John", "last_name": "Doe", "age": 30}
# Print the original dictionary
print("Original dictionary:", my_dict)
# Change the key 'first_name' to 'given_name'
my_dict["given_name"] = my_dict.pop("first_name")
# Print the modified dictionary
print("Modified dictionary:", my_dict)
In our code example, we define a dictionary my_dict with three key-value pairs.
We then print the original dictionary for reference.
To change the key 'first_name' to 'given_name', we use the pop method. This removes the key 'first_name' and returns its value, which is then assigned to a new key 'given_name'.
Finally, we print the modified dictionary to observe the changes.
Output:
Traverse Through the Dictionary Using a for Loop and Change the Key in a Dictionary in Python
One effective way to change a key is by traversing the dictionary using a for loop. This method is particularly useful when the modification criteria are complex or when multiple keys need to be changed based on certain conditions.
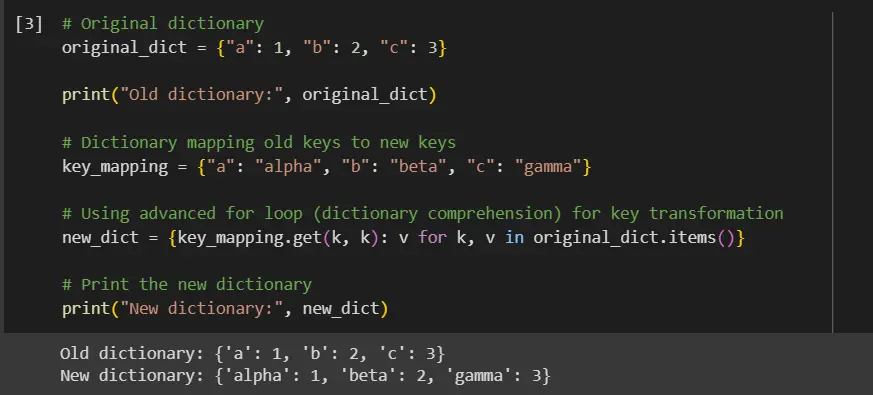
# Original dictionary
original_dict = {"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3}
print("Old dictionary:", original_dict)
# Dictionary mapping old keys to new keys
key_mapping = {"a": "alpha", "b": "beta", "c": "gamma"}
# Using advanced for loop (dictionary comprehension) for key transformation
new_dict = {key_mapping.get(k, k): v for k, v in original_dict.items()}
# Print the new dictionary
print("New dictionary:", new_dict)
In our code analysis, we begin with original_dict, which contains our initial key-value pairs. The key_mapping dictionary serves as our guide for transforming old keys into new keys.
We then employ dictionary comprehension, a compact and advanced form of a for loop, to iterate over original_dict. During each iteration, we use key_mapping.get(k, k) to fetch the new key for each original key k, defaulting to k if it isn’t found in key_mapping.
This process ensures that each key in original_dict is either replaced by its corresponding new key or retained if no replacement is specified.
We thus create new_dict, a new dictionary that reflects these key transformations while preserving the original values.
Our final step is to print new_dict, showcasing the results of our key transformation logic.
Output:
Rebuild an Entirely New Instance in Python
Since dictionary keys are immutable, directly altering them is not feasible. An effective solution is to rebuild a new dictionary instance, allowing us to change the keys while preserving the original dictionary’s structure and values.
Here is an example that demonstrates this.
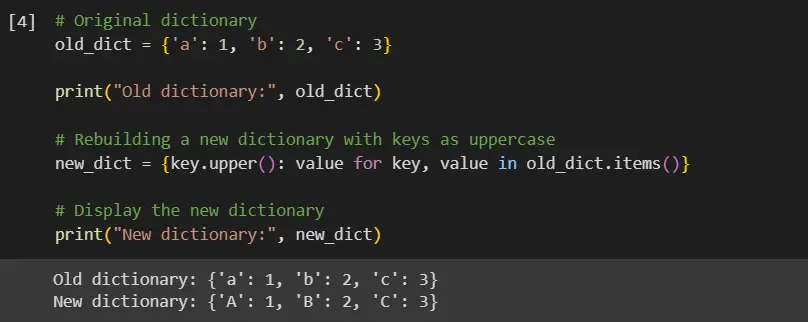
# Original dictionary
old_dict = {"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3}
print("Old dictionary:", old_dict)
# Rebuilding a new dictionary with keys as uppercase
new_dict = {key.upper(): value for key, value in old_dict.items()}
# Display the new dictionary
print("New dictionary:", new_dict)
We begin with an old_dict that has lowercase keys.
Next, we use dictionary comprehension to systematically iterate through the key-value pairs in old_dict. The expression for key, value in old_dict.items() aids in this process, enabling us to access each key-value pair separately.
The transformation of each key is achieved using the expression key.upper(), where the upper() method is applied to convert each key to uppercase. This newly transformed key, along with its original value, forms a new key-value pair in our new_dict.
We repeat this process for each key-value pair in old_dict, leading to the creation of a new_dict where the keys have been transformed to uppercase while the original values remain intact.
Finally, we display new_dict, showcasing the transformed keys in their uppercase format.
Output:
Use the OrderedDict Class in Python
The OrderedDict class from Python’s collections module offers an alternative approach to modifying keys in a dictionary while preserving the order of elements. This feature is particularly useful when the sequence of items is as important as the key-value relationships themselves.
Here’s an example you can follow.
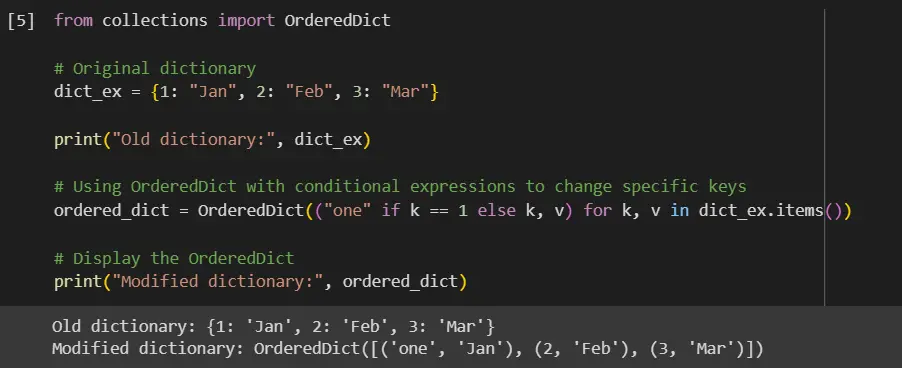
from collections import OrderedDict
# Original dictionary
dict_ex = {1: "Jan", 2: "Feb", 3: "Mar"}
print("Old dictionary:", dict_ex)
# Using OrderedDict with conditional expressions to change specific keys
ordered_dict = OrderedDict(("one" if k == 1 else k, v) for k, v in dict_ex.items())
# Display the OrderedDict
print("Modified dictionary:", ordered_dict)
In our approach, we begin by importing the OrderedDict class from the collections module. We then define a regular dictionary named dict_ex, assigning it numeric keys and string values representing months.
To modify specific keys in our dictionary, we create an OrderedDict using a concise and powerful generator expression. This expression, ("one" if k == 1 else k, v), iterates through each key-value pair in dict_ex.items().
As we iterate, we check whether each key k equals 1. If this condition is met, we replace the key with the string "one"; otherwise, we keep the original key.
Finally, we print the newly created OrderedDict.
Output:
Use the Pandas.DataFrame Function in Python
Renaming dictionary keys is a common task, especially when dictionaries represent columns in a dataset. The goal might be to standardize column names, make them more readable, or align them with certain naming conventions.
To change dictionary keys using Pandas, we typically convert the dictionary to a DataFrame, rename the columns, and then convert it back to a dictionary if needed.
Check this example program.
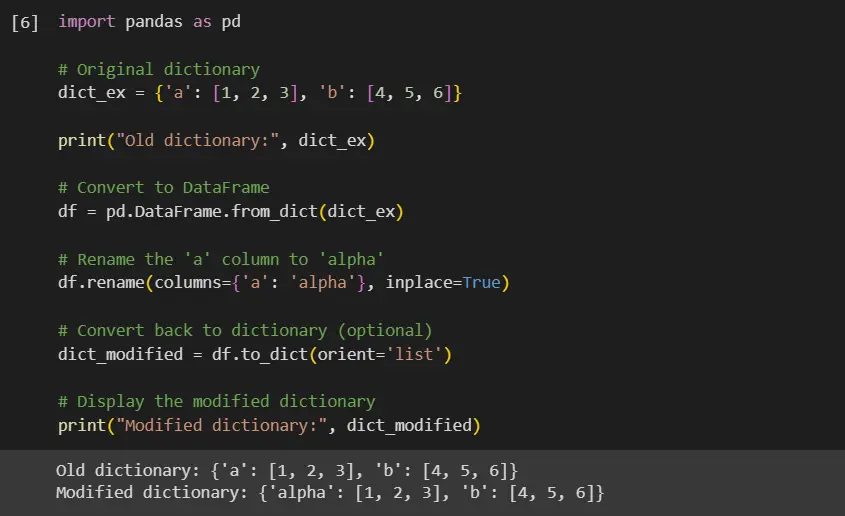
import pandas as pd
# Original dictionary
dict_ex = {"a": [1, 2, 3], "b": [4, 5, 6]}
print("Old dictionary:", dict_ex)
# Convert to DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(dict_ex)
# Rename the 'a' column to 'alpha'
df.rename(columns={"a": "alpha"}, inplace=True)
# Convert back to dictionary (optional)
dict_modified = df.to_dict(orient="list")
# Display the modified dictionary
print("Modified dictionary:", dict_modified)
We begin by importing the Pandas library.
We define a dictionary dict_ex with keys 'a' and 'b'.
This dictionary is then converted into a Pandas DataFrame df.
Using the rename method of DataFrame, we change the column name from 'a' to 'alpha'.
Optionally, we convert the DataFrame back to a dictionary with the to_dict method, specifying the orient='list' to maintain the structure.
Finally, the modified dictionary is printed.
Output:
Conclusion
We began with the basic approach of assigning a new key and deleting the old key, which is straightforward but effective for simple changes. The pop() function offers a more streamlined method, particularly useful when removing the old key is also a requirement.
For scenarios involving complex criteria or multiple key changes, looping through the dictionary with a for loop or using dictionary comprehension provides a robust solution. Rebuilding a new dictionary instance is an elegant way to transform keys while preserving the original structure and values.
The OrderedDict class from the collections module is particularly helpful for maintaining the order of elements, which is crucial in certain applications.
Lastly, we delved into using Pandas for renaming keys, an approach that shines in data manipulation and transformation tasks, especially when dealing with datasets represented as dictionaries. Each method has its own use case, making this collection of techniques a valuable toolkit for Python programmers dealing with dictionary key modifications.