How to Use the @ Symbol in PowerShell
-
Use the
@Symbol to Create an Array in PowerShell -
Use the
@Symbol to Create a Hash Table in PowerShell -
Use the
@Symbol for Here-Strings in PowerShell -
Use the
@Symbol to Perform Splatting With Arrays in PowerShell -
Use the
@Symbol to Perform Splatting With Hash Tables in PowerShell - Conclusion

PowerShell, a powerful scripting language and command-line shell, is known for its flexibility and extensive feature set. One of the lesser-known but incredibly potent features of PowerShell is the use of the @ symbol.
This article delves into the multifaceted applications of the @ symbol in PowerShell scripting, revealing its capabilities in creating arrays, hash tables, and here-strings, particularly in the advanced technique of splatting. Splatting, a method of passing parameters to functions and cmdlets, significantly enhances script readability and maintainability.
By exploring these uses of the @ symbol, the article serves as a comprehensive guide for both beginners and seasoned PowerShell users seeking to harness the full potential of this scripting language.
Use the @ Symbol to Create an Array in PowerShell
In PowerShell, the @ symbol is versatile, but one of its fundamental roles is in the creation and manipulation of arrays. Arrays are essential in any programming language, serving as a way to store and manipulate a collection of elements.
PowerShell’s @ symbol provides a clear and concise method for defining arrays, ensuring that even single elements or results from commands are treated as arrays.
Example:
# Define a simple Print function
function Print($message) {
Write-Host $message
}
# Create an array of numbers
$numbers = @(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
# Iterate over the array and print each number
foreach ($number in $numbers) {
Print $number
}
In this script, we first define a function Print that takes a single parameter $message and uses Write-Host to display it. This function serves as a basic output mechanism for our demonstration.
Next, we create an array, $numbers, using the @ symbol. This array is initialized with five numbers: 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5.
Notice the use of @() around the numbers, ensuring they are treated as an array.
Following the array creation, we use a foreach loop to iterate over each element in the $numbers array. Inside the loop, we call our Print function, passing each number in turn.
Output:

Use the @ Symbol to Create a Hash Table in PowerShell
A hash table is a compact data structure that stores one or more paired keys and values. It is also known as a dictionary or associative array.
The syntax to create a hash table in PowerShell begins with the @ symbol. The keys and values are enclosed in the {} brackets.
Example:
# Define a simple Print function
function Print($message) {
Write-Host $message
}
# Create a hashtable of employee details
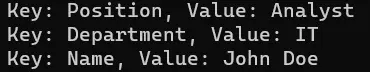
$employee = @{
Name = 'John Doe'
Department = 'IT'
Position = 'Analyst'
}
# Iterate over the hashtable and print each detail
foreach ($key in $employee.Keys) {
$value = $employee[$key]
Print "Key: $key, Value: $value"
}
In this script, we begin by defining a Print function, which is a basic utility to output messages to the host.
Next, we create a hashtable $employee using the @ symbol. This hashtable contains three key-value pairs representing an employee’s name, department, and position.
After defining the hashtable, we use a foreach loop to iterate through each key in the hashtable. Inside the loop, we retrieve the value corresponding to each key and then use our Print function to output both the key and its value.
Output:
Use the @ Symbol for Here-Strings in PowerShell
Another important use of the @ symbol is to define here-strings in PowerShell. Quotation marks are interpreted literally in a here-string.
The primary purpose of here-strings in PowerShell is to simplify the handling of long strings, particularly those that require specific formatting, line breaks, or special characters. Regular string handling in PowerShell, using single quotes ' or double quotes ", can become cumbersome with multi-line texts.
Example:
# Define a simple Print function
function Print($message) {
Write-Host $message
}
# Define a variable
$name = "John"
# Create an expandable here-string
$multiLineText = @"
Hello, $name!
Welcome to PowerShell scripting.
This is an example of a multi-line here-string.
"@
# Print the here-string
Print $multiLineText
In this script, we begin by defining a Print function for displaying output.
We then define a variable $name set to John. Following this, we create an expandable here-string $multiLineText.
Notice how the @" "@ delimiters are used to start and end the multi-line string. Inside this here-string, the variable $name is included, which will be expanded to its value.
Finally, we call the Print function to output the content of our here-string.
Output:
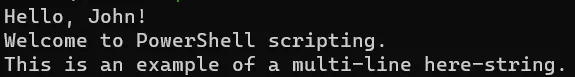
A here-string contains all the texts between @" "@.
Here-string with single quotes:
# Define a simple Print function
function Print($message) {
Write-Host $message
}
# Create a single-quoted here-string
$literalText = @'
This is an example of a single-quoted here-string.
Special characters like $ or ` won't be processed.
Everything here is treated as literal text.
'@
# Print the here-string
Print $literalText
In our script, we start with defining a Print function that outputs a given message to the host.
Next, we create a single-quoted here-string named $literalText. The @' '@ delimiters indicate the start and end of the here-string.
Within these delimiters, we include text that mentions special characters like $ and backtick ```, which would normally have special meanings in PowerShell.
Finally, we call the Print function to display the content of our here-string.
Output:
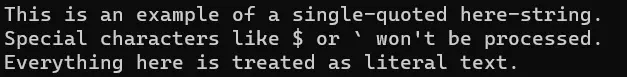
In single-quote here-strings, variables are interpreted literally and printed in the output, but not in double-quotes here-strings.
Use the @ Symbol to Perform Splatting With Arrays in PowerShell
Splatting is primarily used to enhance script readability and maintainability, especially when dealing with commands that require a large number of parameters. Rather than listing each parameter and its value directly in the command, splatting allows you to define them in an array or hashtable and pass them all at once using the @ symbol.
You can use the @ symbol for splatting arrays in the command. The @ symbol can use an array to splat values for position parameters that do not need the names of parameters.
Example:
# Define a simple Print function
function Print-Message($part1, $part2, $part3) {
Write-Host "$part1 - $part2 - $part3"
}
# Define an array of parameters
$paramArray = @('Hello', 'PowerShell', 'Splatting')
# Call the function using splatting
Print-Message @paramArray
In this example, we start by defining a Print-Message function that takes three parameters and outputs them in a formatted string.
We then create an array $paramArray containing three string values: Hello, PowerShell, and Splatting. These values correspond to the parameters $part1, $part2, and $part3 of our function.
When calling the Print-Message function, we use splatting to pass the array of parameters. The @ symbol before $paramArray indicates that the elements of the array should be mapped to the function’s parameters in their respective order.
Output:

Use the @ Symbol to Perform Splatting With Hash Tables in PowerShell
Similarly, you can use the @ symbol for hash table splatting.
The primary purpose of splatting with hash tables is to simplify the process of passing parameters to functions and cmdlets in PowerShell. It becomes particularly valuable in managing complex commands with numerous parameters, enhancing code readability and maintainability.
Splatting allows for a more structured and cleaner way of specifying parameters, which is beneficial in script debugging and editing.
Example:
# Define a simple function
function Get-Greeting {
param (
[string]$Name,
[string]$TimeOfDay
)
"Good $TimeOfDay, $Name!"
}
# Define a hash table of parameters
$greetingParams = @{
Name = 'Alice'
TimeOfDay = 'Morning'
}
# Call the function using splatting
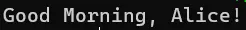
$greeting = Get-Greeting @greetingParams
Write-Host $greeting
In our script, we first define a function Get-Greeting that accepts two parameters: Name and TimeOfDay.
Next, we create a hash table $greetingParams and populate it with keys Name and TimeOfDay, assigning them the values 'Alice' and 'Morning', respectively. These keys correspond to the parameter names of the Get-Greeting function.
When calling Get-Greeting, we use splatting by prefixing the hash table variable $greetingParams with the @ symbol. This action maps the keys of the hash table to the corresponding parameters of the function.
Output:
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we have explored the versatile applications of the @ symbol in PowerShell, an aspect that often goes unnoticed but holds immense potential in scripting. From creating arrays and hash tables to defining here-strings and implementing splatting, the @ symbol is a small yet powerful tool in a PowerShell scripter’s arsenal.
Its ability to simplify complex parameter passing and enhance code readability is particularly notable in the context of splatting with arrays and hash tables. As we have seen, the use of the @ symbol in PowerShell is not just a matter of syntax but a gateway to more efficient, readable, and maintainable scripting practices.
