How to Deserialize XML to Object in C#
- Use Manually Typed Classes to Deserialize XML File to C# Object
-
Use the
Paste SpecialFeature of Visual Studio to DeserializeXmlto C# Object -
Use the
XSD toolto DeserializeXMLto C# Object
This article will demonstrate the conversion or deserializing of XML files into the C# object.
Use Manually Typed Classes to Deserialize XML File to C# Object
- C# is associated with
classesandobjectsalong withattributesandmethods. Objectsare represented with classes programmatically, such asJohnorJames.Attributesare characteristics of objects such as thecolor of a car,year of production,age of a person,orcolor of a building.XMLis the standardized format that allowsXMLdata to be parsed irrespective of the medium of transmitting theXMLfile.
Further discussion is available via this reference.
Below is an XML code sample that would be converted to a C# object.
1. <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2. <Company xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
3. <Employee name="x" age="30" />
4. <Employee name="y" age="32" />
5. </Company>
A class with a similar structure would be created in C# to convert the XML code sample.
using System.Xml.Serialization;
[XmlRoot(ElementName = "Company")]
public class Company
{
public Company() {
Employees = new List<Employee>();
}
[XmlElement(ElementName = "Employee")]
public List<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
public Employee this[string name] {
get {
return Employees.FirstOrDefault(
s => string.Equals(s.Name, name, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase));
}
}
}
public class Employee {
[XmlAttribute("name")]
public string Name { get; set; }
[XmlAttribute("age")] public string Age { get; set; }
}
The final step to convert the XML object to C# is to use the System.Xml.Serialization.XmlSerializer function to serialize the object.
public T DeserializeToObject<T>(string filepath)
where T : class {
System.Xml.Serialization.XmlSerializer ser =
new System.Xml.Serialization.XmlSerializer(typeof(T));
using (StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(filepath)) {
return (T)ser.Deserialize(sr);
}
}
Use the Paste Special Feature of Visual Studio to Deserialize Xml to C# Object
This method requires using the Microsoft Visual Studio 2012 and above with .Net Framework 4.5 and above. The WCF workload for Visual Studio must also be installed.
- The content of the
XMLdocument must be copied to the clipboard. - Add a new
emptyclass to the project solution. - Open the new class file.
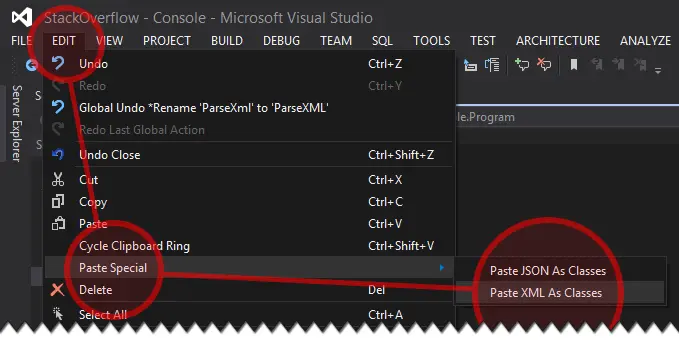
- Click on the
Editbutton on the menu bar of the IDE. - Select
Paste Specialfrom the dropdown. - Click on Paste XML As Classes.
To use the class generated by Visual Studio, create the Helpers class.
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Web.Script.Serialization; // Add reference: System.Web.Extensions
using System.Xml;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
namespace Helpers {
internal static class ParseHelpers
{
private static JavaScriptSerializer json;
private static JavaScriptSerializer JSON {
get { return json ?? (json = new JavaScriptSerializer()); }
}
public static Stream ToStream(this string @this) {
var stream = new MemoryStream();
var writer = new StreamWriter(stream);
writer.Write(@this);
writer.Flush();
stream.Position = 0;
return stream;
}
public static T ParseXML<T>(this string @this)
where T : class {
var reader = XmlReader.Create(
@this.Trim().ToStream(),
new XmlReaderSettings() { ConformanceLevel = ConformanceLevel.Document });
return new XmlSerializer(typeof(T)).Deserialize(reader) as T;
}
public static T ParseJSON<T>(this string @this)
where T : class {
return JSON.Deserialize<T>(@this.Trim());
}
}
}
Use the XSD tool to Deserialize XML to C# Object
XSD is used to automatically generate classes or objects equivalent to the schema defined in an XML file or document.
XSD.exe is normally found in the path: C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\Windows\{version}\bin\NETFX {version} Tools\. Further discussion is available via this reference.
Suppose the XML file is saved in this path: C:\X\test.XML.
Below are the steps to follow to deserialize the XML to C# classes automatically:
- Type
Developer Command Promptinto the search bar and click on it to open. - Type
cd C:\Xto navigate to theXMLfile path. - Remove line numbers and any unnecessary characters in the
XMLfile. - Type
xsd test.XMLto create anXSD fileequivalent from the test.XML. - A
test.XSDfile is created in the same file path. - Type
XSD /c test.XSDto create theC# classesequivalent to theXMLfile. - A
test.csfile is created, a C# class with an exact schema of theXMLfile.
Output:
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// <auto-generated>
// This code was generated by a tool.
// Runtime Version:4.0.30319.42000
//
// Changes to this file may cause incorrect behavior and will be lost if
// the code is regenerated.
// </auto-generated>
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
using System.Xml.Serialization;
//
// This source code was auto-generated by xsd, Version=4.8.3928.0.
//
/// <remarks/>
[System.CodeDom.Compiler.GeneratedCodeAttribute("xsd", "4.8.3928.0")]
[System.SerializableAttribute()]
[System.Diagnostics.DebuggerStepThroughAttribute()]
[System.ComponentModel.DesignerCategoryAttribute("code")]
[System.Xml.Serialization.XmlTypeAttribute(AnonymousType=true)]
[System.Xml.Serialization.XmlRootAttribute(Namespace="", IsNullable=false)]
public partial class Company {
private CompanyEmployee[] itemsField;
/// <remarks/>
[System.Xml.Serialization.XmlElementAttribute("Employee", Form=System.Xml.Schema.XmlSchemaForm.Unqualified)]
public CompanyEmployee[] Items {
get {
return this.itemsField;
}
set {
this.itemsField = value;
}
}
}
/// <remarks/>
[System.CodeDom.Compiler.GeneratedCodeAttribute("xsd", "4.8.3928.0")]
[System.SerializableAttribute()]
[System.Diagnostics.DebuggerStepThroughAttribute()]
[System.ComponentModel.DesignerCategoryAttribute("code")]
[System.Xml.Serialization.XmlTypeAttribute(AnonymousType=true)]
public partial class CompanyEmployee {
private string nameField;
private string ageField;
/// <remarks/>
[System.Xml.Serialization.XmlAttributeAttribute()]
public string name {
get {
return this.nameField;
}
set {
this.nameField = value;
}
}
/// <remarks/>
[System.Xml.Serialization.XmlAttributeAttribute()]
public string age {
get {
return this.ageField;
}
set {
this.ageField = value;
}
}
}
