How to Create Dropdown Menu in Tkinter

It has some methods to create a dropdown menu in Tkinter.
- Use Combobox as introduced in the Tkinter tutorial Combobox chapter.
- Use
OptionMenuWidget.
The OptionMenu is similar to the Combobox widget but is already included in the Tkinter itself; therefore, you don’t need to import ttk module like in the case of Combobox.
We will introduce how to create a dropdown menu with the OptionMenu widget in this article.
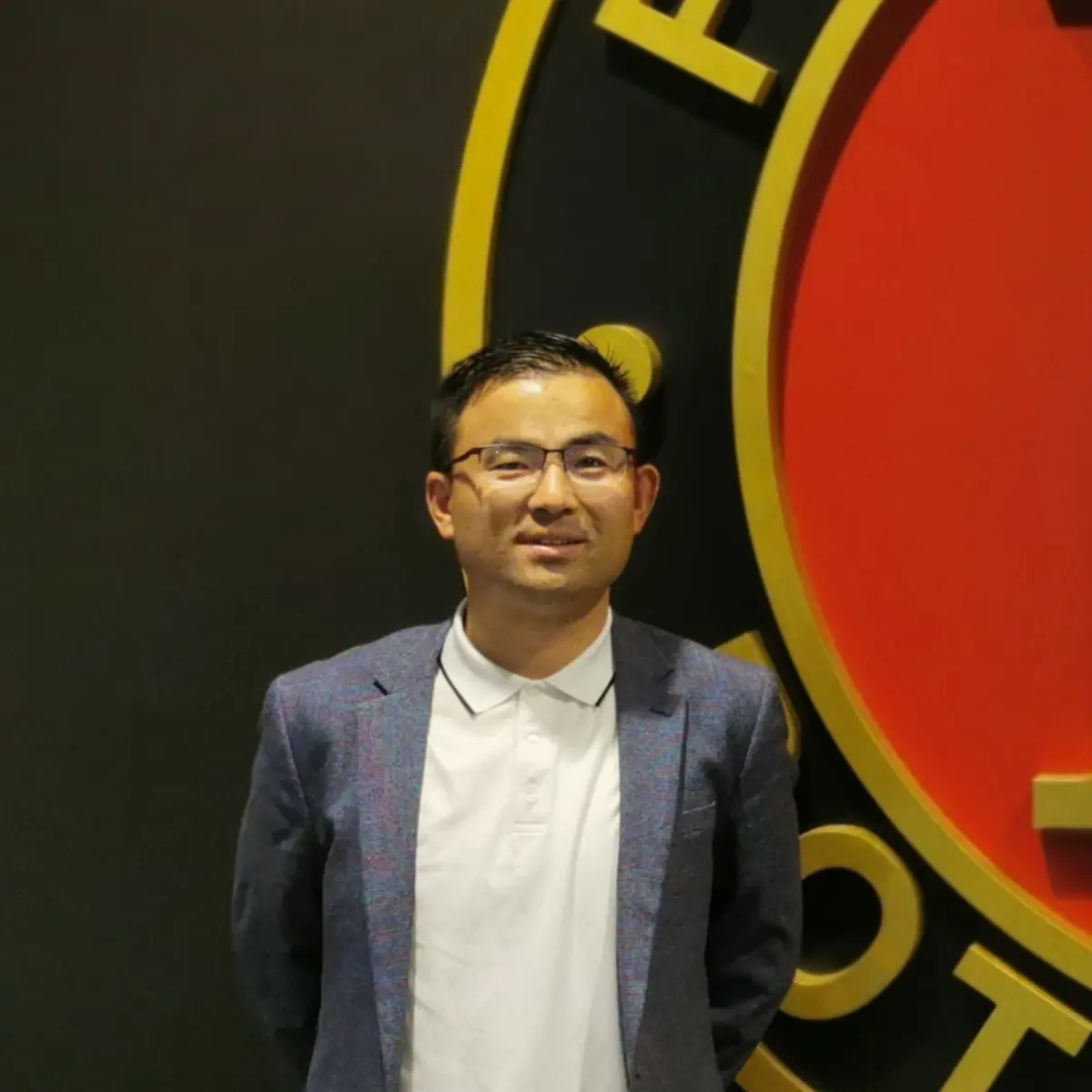
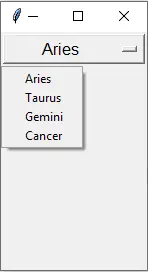
Tkinter OptionMenu Example
import tkinter as tk
OptionList = ["Aries", "Taurus", "Gemini", "Cancer"]
app = tk.Tk()
app.geometry("100x200")
variable = tk.StringVar(app)
variable.set(OptionList[0])
opt = tk.OptionMenu(app, variable, *OptionList)
opt.config(width=90, font=("Helvetica", 12))
opt.pack()
app.mainloop()
opt = tk.OptionMenu(app, variable, *OptionList)
app is the parent of the created option menu,
variable is the initial text variable that has tk.StringVar type.
*OptionList is the other menu options. * is used for unpacking the container as list type here.
Bind Command to OptionMenu When Value Changes
OptionMenu couldn’t link a command when a new value is selected from the option list. You couldn’t simply link a callback function to it like button widget
tk.Button(app, text="Increase", width=30, command=change_label_number)
You need to use a trace method to attach observer callbacks to the OptionMenu variable. Every time the variable changes, it triggers the callback functions.
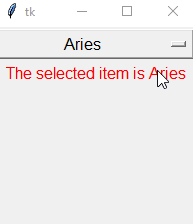
OptionMenu Callback Example
import tkinter as tk
OptionList = ["Aries", "Taurus", "Gemini", "Cancer"]
app = tk.Tk()
app.geometry("100x200")
variable = tk.StringVar(app)
variable.set(OptionList[0])
opt = tk.OptionMenu(app, variable, *OptionList)
opt.config(width=90, font=("Helvetica", 12))
opt.pack(side="top")
labelTest = tk.Label(text="", font=("Helvetica", 12), fg="red")
labelTest.pack(side="top")
def callback(*args):
labelTest.configure(text="The selected item is {}".format(variable.get()))
variable.trace("w", callback)
app.mainloop()
The trace observer has three modes,
observer mode |
Explanation |
|---|---|
w |
when variable is written by someone |
r |
when variable is read by someone |
u |
when variable is deleted |
Then variable.trace("w", callback) means it will call callback function when variable is written or selected by the user.
Founder of DelftStack.com. Jinku has worked in the robotics and automotive industries for over 8 years. He sharpened his coding skills when he needed to do the automatic testing, data collection from remote servers and report creation from the endurance test. He is from an electrical/electronics engineering background but has expanded his interest to embedded electronics, embedded programming and front-/back-end programming.
LinkedIn Facebook