The History Command in Linux
-
the
historyCommand in Bash -
the
historyEnvironment Variables in Bash - Show History in Bash
-
Show the First
nCommands in History in Bash -
Show the Last
nCommands in History in Bash - Search in History in Bash
- Remove Command From History in Bash
- Remove the Whole History in Bash
This tutorial shows using the history command to display the Bash history, search in history, remove commands, and clear the whole history.
the history Command in Bash
The history command in Bash displays a list of all the commands executed on the shell session. The history command treats each command executed on the shell as an event and assigns it an event number.
These commands can later be accessed using the event number, and they can also be modified. The .bash_history file in the home directory also stores the recently executed commands on the terminal.
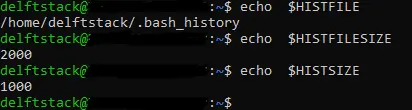
the history Environment Variables in Bash
Three environment variables related to the history command are; HISTFILE, HISTFILESIZE and HISTSIZE. The environment variable, HISTFILE, stores the Bash history file’s name and location, .bash_history.
The environment variable, HISTFILESIZE, stores the number of commands stored in the .bash_history file and the HISTSIZE stores the number of commands that can be cached.
The image below shows the values stored in the three environment variables; HISTFILE, HISTFILESIZE and HISTSIZE.
The .bash_history file can store 2000 commands, and once the maximum number of commands is reached, the oldest commands will be removed, and the new commands will be stored.
The maximum number of commands that the system can cache is 1000.
You must edit the .bashrc file in your home directory to modify the three environment variables.
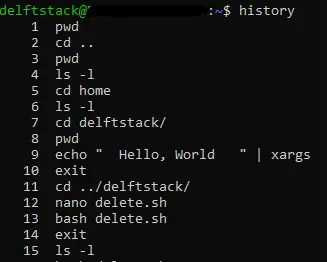
Show History in Bash
To display all the history commands in Bash, type history and press Enter. We see part of the output displayed to the standard terminal when executing the history command in the image below.
The number that precedes the command is the event number associated with each command.

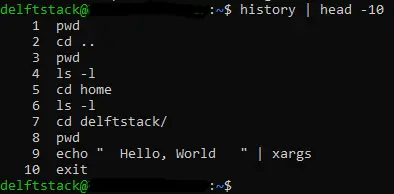
Show the First n Commands in History in Bash
We can use the history command and the head command to display the first n commands in history. We display the first 10 commands in history in the image below.
We use the history command, the pipe operator and the head command to display the first 10 commands. The history command output is piped to the head command, which only takes the first 10 lines of the history output and displays them to the standard output.
Show the Last n Commands in History in Bash
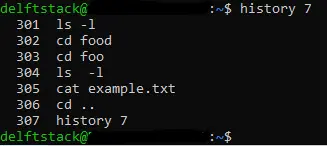
We can use the history command to display the last n commands and pass an integer as an argument. The integer we passed tells the history command to display the last n commands from history.
We use the history command and pass the integer 7 in the image below. It means that the history command will display the last 7 commands from history.
Search in History in Bash
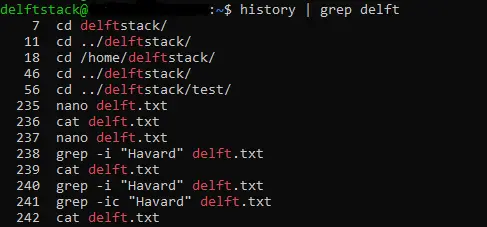
We can also search for a particular pattern in history using the history command with the grep command. The image below searches for the regular expression delft using the grep command in history.
We use the history command, the pipe operator, and the grep command to search for the regular expression in history. The output of the history command is piped to the grep command, which searches for the regular expression, delft, in it.
All the lines that match the regular expression are displayed to the standard terminal.
Remove Command From History in Bash
The history command can also remove a specific command from history. To remove a command from history, we use the history command with the -d option and the event number of the command.
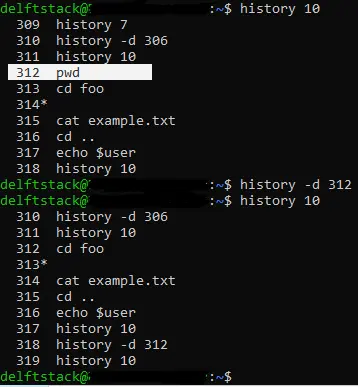
In the image below, we use the command history 10 to list the last 10 commands in history. We have decided to remove the command that has been highlighted.
We use the history command with the -d option, and we pass in the event number of the highlighted command. It removes the command from history.
To confirm if the command has been removed, we check the last 10 lines in history, and we see that the command pwd, which had the event id of 312, is not there.
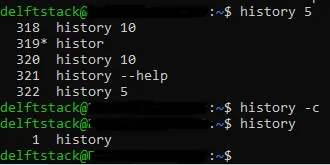
Remove the Whole History in Bash
To remove all entries in history, we use the history command with the -c option. It removes all the entries in history.
In the image below, we use the history command to list the last 5 commands in history. Later, we use the history command with the -c option to clear all entries in history.
We use the history command to display all entries in history, and we see that all the entries have been cleared.