在 Java 中比较数组
Mehvish Ashiq
2023年10月12日
Java
Java Array
-
在 Java 中使用
==运算符比较数组 -
使用
Arrays.equals()方法比较 Java 中的数组 -
使用
Arrays.deepEquals()方法比较 Java 中的数组 -
使用
for循环比较 Java 中的数组
今天,我们将编写不同的代码片段来比较 Java 中的数组。我们将看到如何使用 == 运算符、Arrays.equals()、Arrays.deepEquals() 以及包含 for 循环的自定义函数来比较 Java 中的数组。
在 Java 中使用 == 运算符比较数组
示例代码:
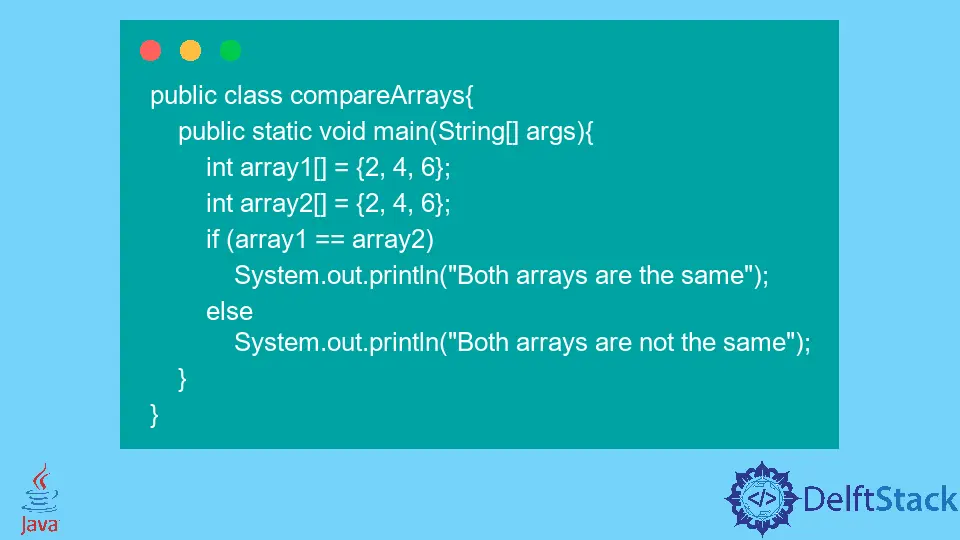
public class compareArrays {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int array1[] = {2, 4, 6};
int array2[] = {2, 4, 6};
if (array1 == array2)
System.out.println("Both arrays are the same");
else
System.out.println("Both arrays are not the same");
}
}
输出:
Both arrays are not the same
在 main 函数中,我们有两个数组 array1 和 array2,指的是两个不同的对象。因此,比较两个不同的参考变量,导致 Both arrays are not the same。
使用 Arrays.equals() 方法比较 Java 中的数组
示例代码:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class compareArrays {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int array1[] = {2, 4, 6};
int array2[] = {2, 4, 6};
if (Arrays.equals(array1, array2))
System.out.println("Both arrays are the same");
else
System.out.println("Both arrays are not the same");
}
}
输出:
Both arrays are the same
这个 main 方法还包含两个名为 array1 和 array2 的数组。在这里,我们使用位于 Arrays Class 中的 Arrays.equals() 方法并获取两个数组并比较它们的内容。
假设我们有两个需要比较的二维数组。我们能否利用上面给出的相同方法进行深度比较?不。
在 Java Arrays 类中,我们有各种基本类型的 equals() 方法,例如 int、char 等。Object 类有一个 equals() 方法,但我们不能使用它对二维数组进行深度比较。
示例代码:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class compareArrays {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int innerArray1[] = {2, 4, 6};
int innerArray2[] = {2, 4, 6};
Object outerArray1[] = {innerArray1};
Object outerArray2[] = {innerArray2};
if (Arrays.equals(outerArray1, outerArray2))
System.out.println("Both arrays are the same");
else
System.out.println("Both arrays are not the same");
}
}
输出:
Both arrays are not the same
我们可以使用 deepEquals() 方法进行深度比较,如果我们有二维数组,这将很有帮助。
使用 Arrays.deepEquals() 方法比较 Java 中的数组
示例代码:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class compareArrays {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int innerArray1[] = {2, 4, 6};
int innerArray2[] = {2, 4, 6};
Object outerArray1[] = {innerArray1};
Object outerArray2[] = {innerArray2};
if (Arrays.deepEquals(outerArray1, outerArray2))
System.out.println("Both arrays are the same");
else
System.out.println("Both arrays are not the same");
}
}
输出:
Both arrays are the same
deepEquals() 方法适用于深度比较。Arrays.deepEquals() 方法检查两个数组是否相等。
这两个数组可以是一维的、二维的,甚至是多维的。
此方法如何确定提供的数组是否相等?为此,你必须牢记以下几点:
- 如果两个提供的数组的引用均为空,则数组将非常相等。
- 如果两个数组引用指向包含确切元素数量和对应元素对的数组,我们可以声明它们完全相等。
- 如果以下列表中的任何一个条件成立,则可能为 null 的两个元素
element1和element2将完全相等:- 如果两个数组的类型都是对象引用,则
Arrays.deepEquals(element1, element2)返回 true。 - 如果两个数组都属于精确的原始类型,则
Arrays.equals(element1, element2)返回 true。 element1 == element2element1.equals(element2)返回 true。
- 如果两个数组的类型都是对象引用,则
使用 for 循环比较 Java 中的数组
示例代码:
public class compareArrays {
public static boolean compare(int[] array1, int[] array2) {
boolean flag = true;
if (array1 != null && array2 != null) {
if (array1.length != array2.length)
flag = false;
else
for (int i = 0; i < array2.length; i++) {
if (array2[i] != array1[i]) {
flag = false;
}
}
} else {
flag = false;
}
return flag;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int array1[] = {2, 4, 6};
int array2[] = {2, 4, 6};
if (compare(array1, array2))
System.out.println("Both arrays are the same");
else
System.out.println("Both arrays are not the same");
}
}
输出:
Both arrays are the same
在这里,我们编写了一个 compare() 函数,它将两个数组转换为 int 类型。它使用 for 循环在单个元素级别上比较它们,如果两个数组相同则返回 true;否则为假。
Enjoying our tutorials? Subscribe to DelftStack on YouTube to support us in creating more high-quality video guides. Subscribe
作者: Mehvish Ashiq
