警告を修正: Java で非推奨の API を使用またはオーバーライドします
今日は、警告が非推奨の API を使用またはオーバーライドしていますと表示される理由を確認し、これを修正してタスクを達成する方法を示します。
Java で uses or overrides a deprecated API という警告を修正
コード例 (警告を含む):
// import libraries
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
// Main class
public class Main {
// main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// path of a text file
File filePath = new File("Files/TestFile.txt");
try {
// obtain input bytes from a file
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
// adds the functionality to another input stream
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream);
// lets an app read primitive Java data types from the specified input stream
DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(bufferedInputStream);
if (dataInputStream.available() != 0) {
// Get a line.
String line = dataInputStream.readLine();
// Place words to an array which are split by a "space".
String[] stringParts = line.split(" ");
// Initialize the word's maximum length.
int maximumLength = 1;
// iterate over each stingPart, the next one is addressed as "stringX"
for (String stringX : stringParts) {
// If a document contains the word longer than.
if (maximumLength < stringX.length())
// Set the new value for the maximum length.
maximumLength = stringX.length();
} // end for-loop
// +1 because array index starts from "0".
int[] counter = new int[maximumLength + 1];
for (String str : stringParts) {
// Add one to the number of words that length has
counter[str.length()]++;
}
// We are using this kind of loop because we require the "length".
for (int i = 1; i < counter.length; i++) {
System.out.println(i + " letter words: " + counter[i]);
} // end for-loop
} // end if statement
} // end try
catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} // end catch
} // end main method
} // end Main class
このコードでは、.txt ファイルにアクセスし、そのファイルを 1 行ずつ読み取り、単一の スペース に基づいて分割された配列に単語を配置します。 次に、各単語の文字数をカウントし、それらすべてをプログラム出力に表示します。
このプログラムは出力を生成しますが、String line = dataInputStream.readLine(); 行で非推奨の API を使用またはオーバーライドしていることも強調しています。 以下を参照してください。
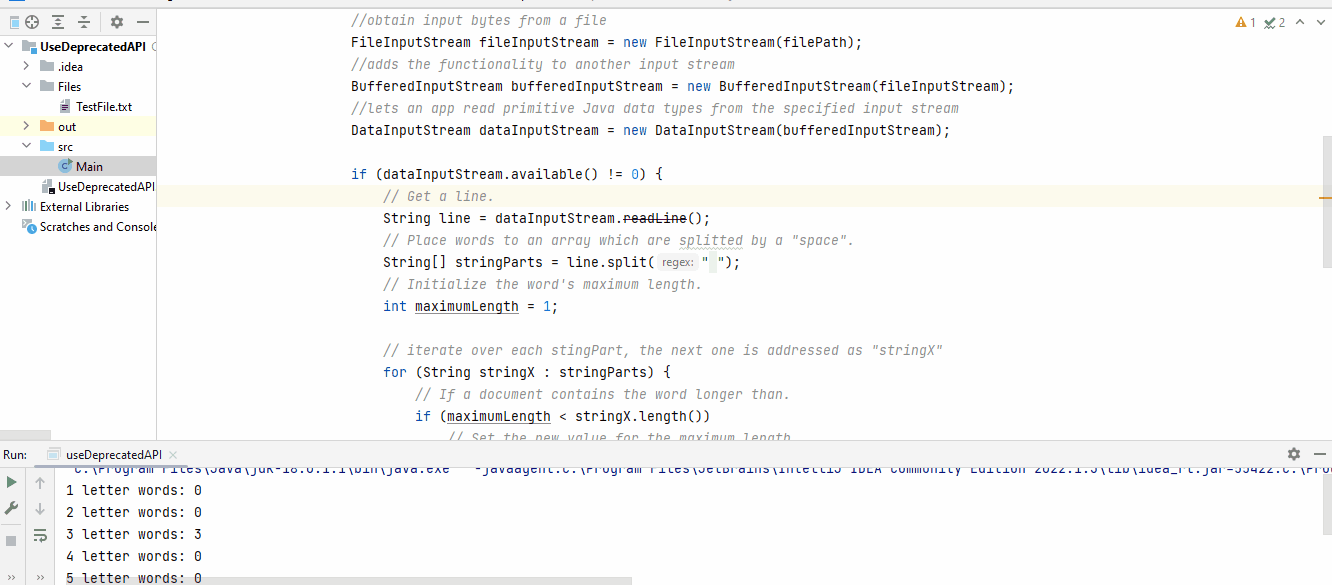
この警告は、DataInputStream クラスの readLine() メソッドを使用して生成されています。 ドキュメント によると、このメソッドは、バイトを文字に適切に変換しないため、JDK 1.1 以降非推奨になっています。
ただし、このメソッドは推奨されておらず、場合によっては期待どおりに動作する可能性があります。 しかし、それがもはやその役目を果たすことを保証することはできません。
したがって、類似しているが一貫した方法を使用することをお勧めします。
JDK 1.1 の時点で、テキストの行を読み取るために推奨される方法は BufferedReader クラスの readLine() 関数です。 すべてのコードを最初から変更する必要はありませんが、DataInputStream を BufferedReader クラスに変換するだけで済みます。
次のコード行を置き換えます。
DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(in);
このコード行で:
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
これで、完全な作業プログラムは次のようになります。
// import libraries
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
// Main class
public class Main {
// main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// path of a text file
File filePath = new File("Files/TestFile.txt");
try {
// obtain input bytes from a file
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
// adds the functionality to another input stream
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream);
// lets an app read primitive Java data types from the specified input stream
// DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(bufferedInputStream);
BufferedReader bufferedReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(bufferedInputStream));
String line = "";
// get a line and check if it is not null
if ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
// Place words to an array which are split by a "space".
String[] stringParts = line.split(" ");
// Initialize the word's maximum length.
int maximumLength = 1;
// iterate over each stingPart, the next one is addressed as "stringX"
for (String stringX : stringParts) {
// If a document contains the word longer than.
if (maximumLength < stringX.length())
// Set the new value for the maximum length.
maximumLength = stringX.length();
} // end for-loop
// +1 because array index starts from "0".
int[] counter = new int[maximumLength + 1];
for (String str : stringParts) {
// Add one to the number of words that length has
counter[str.length()]++;
}
// We are using this kind of loop because we require the "length".
for (int i = 1; i < counter.length; i++) {
System.out.println(i + " letter words: " + counter[i]);
} // end for-loop
} // end if statement
} // end try
catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} // end catch
} // end main method
} // end Main class
さらに、次のようなものも表示される場合。
Recompile with -Xlint: deprecation for details
心配しないで; 非推奨のものをどこで使用しているかについての詳細を得るために、コンパイル中に使用するオプションを示しているだけです。
