How to Bind Enter Key to a Function in Tkinter
- Bind Event to a Function
- Bind Key Press to a Function
- Bind Key Press to a Function in Class Method Example
In this tutorial, We will introduce how to bind Enter key to a function in Tkinter.
Bind Event to a Function
The Enter key pressing is an event, like button clicking, and we could bind functions or methods to this event to make the event trigger the specified function.
widget.bind(event, handler)
If the event occurs, it will trigger the handler automatically.
Bind Key Press to a Function
import tkinter as tk
app = tk.Tk()
app.geometry("200x100")
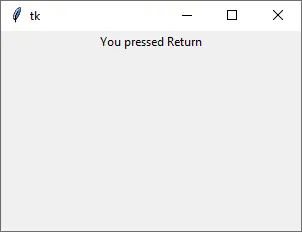
def callback(event):
label["text"] = "You pressed Enter"
app.bind("<Return>", callback)
label = tk.Label(app, text="")
label.pack()
app.mainloop()
def callback(event):
label["text"] = "You pressed Enter"
The event is a hidden argument passed to the function. It will raise TypeError if you don’t give it in the function input argument.
app.bind("<Return>", callback)
We bind the callback function to the <Return> event, or in other words, Enter key pressing event.
Bind Key Press to a Function in Class Method Example
import tkinter as tk
class app(tk.Frame):
def __init__(self):
self.root = tk.Tk()
self.root.geometry("300x200")
self.label = tk.Label(self.root, text="")
self.label.pack()
self.root.bind("<Return>", self.callback)
self.root.mainloop()
def callback(self, event):
self.label["text"] = "You pressed {}".format(event.keysym)
app()
This class implementation is similar to the above method.
We put the keysym attribute of the event object in the shown Tkinter label.
keysym is the key symbol of the keyboard event. Enter is Return as we introduced above.
Founder of DelftStack.com. Jinku has worked in the robotics and automotive industries for over 8 years. He sharpened his coding skills when he needed to do the automatic testing, data collection from remote servers and report creation from the endurance test. He is from an electrical/electronics engineering background but has expanded his interest to embedded electronics, embedded programming and front-/back-end programming.
LinkedIn Facebook