How to Skip Grant Tables in MySQL

Today, we will learn the MySQL skip grant tables, grant tables, and how to use --skip-grant-tables in MySQL when we lock the root user, forget its password, or want to restore full privileges.
Grant Tables in the MySQL System Database
Grant tables in the MySQL System Database has the following information:
user(global privileges, user accounts, & other non-privileged fields/columns)db(privileges on database level)tables_priv(privileges on table level)columns_priv(privileges on column level)procs_priv(privileges on functions & stored procedures)proxies_priv(privileges on proxy-user)
Every grant table consists of scope and privilege columns. The scope column identifies every row’s scope in a table.
The privilege column represents the privileges granted by a table row or the kind of operations it allows to perform.
the --skip-grant-tables Option in MySQL
As of MySQL 8.0.3, --skip-grant-tables enabled --skip-networking, which automatically doesn’t allow remote connections. For instance, the SQL statements about the account management, ALTER USER, are disabled when --skip-grant-tables is active.
We can use the --skip-grant-tables in the following situations:
- We accidentally lock the
rootuser. - We forget the
rootpassword. - We lost all the privileges of a
rootuser.
Let’s start learning about the solution for each situation mentioned above.
Use of --skip-grant-tables When the root User Is Locked
-
Stop the MySQL Service in
services.mscusing Windows Administrative Tools. It can be accessed atC:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Administrative Toolsor via the windows search bar.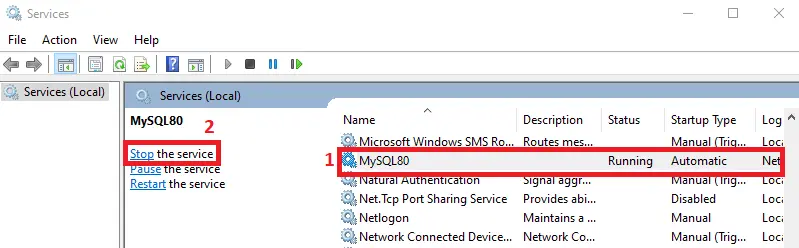
-
Update the
SERVER SECTIONunder[mysqld]in the configuration file namedmy.iniby adding the following line:skip-grant-tables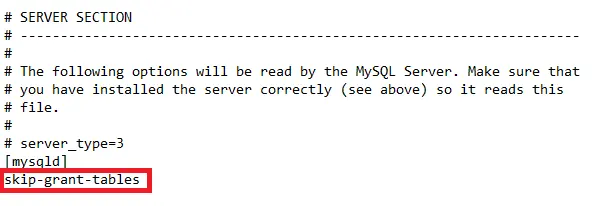
Themy.inifile resides atC:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\my.iniif you have installed MySQL at the default location. -
Start the MySQL server again. This time we can log in without a password.
Use --skip-grant-tables to Restore Full Privileges for the MySQL root User
We can restore full privileges for the MySQL root user by using the UPDATE command.
-
First, we need to stop
mysqld. -
Next, restart it with the
--skip-grant-tableoption to disable the login credentials for therootaccount. -
Further, connect to the
mysqldserver again withmysqlonly. Here we don’t use the-poption for the password and may not enter the username as well. -
Use the following command in the
mysqlclient to get all privileges for arootuser in MySQL.mysql> UPDATE mysql.user SET Grant_priv = 'Y', Super_priv = 'Y' WHERE User = 'root';We have set the super privileges using
Super_priv = 'Y'. -
Now, we have to flush the privileges by using the
FLUSHcommand as follows:mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Remember, when
--skip-grant-tableis active, MySQL does not examine the grant tables upon query and connections, which means anybody can quickly login remotely and manipulate the database.
Use of --skip-grant-tables to Reset root Password in MySQL
Here we can use the mysql client to reset the root password, but it is a less secure approach. To continue with this method, follow the steps given below:
-
Stop MySQL server and restart with
--skip-grant-tables. Why are we shutting down the server? Because it’s an insecure method and disables the remote connections via enabling theskip_networking. -
Reconnect the MySQL Server using the
mysqlclient. The password is not required here. -
In
mysqlclient, reload grant tables to make account management statements work.mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; -
Now, update the password for the
'root'@'localhost'account with your desired password. -
Update the statements to use that hostname to change the
rootaccount’s password with a different hostname part.mysql> ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'NewPassword'; -
Finally, we can connect to MySQL Server as a
rootuser with a new password. Shut down the server and restart as we usually do (without--skip-grant-tablesandskip-networking).
