在 TypeScript 中返回一個 Promise

本教程將討論在 TypeScript 中返回正確的 Promise 以及編碼示例和輸出。讓我們首先看看 Promises 是什麼以及為什麼要使用它們。
TypeScript 中的 Promise
TypeScript 中的 Promise 執行非同步程式設計以同時執行多個任務。我們可以在一次處理大量工作時使用它。
我們可以使用 Promise 跳過當前操作並轉到以下程式碼行。
如果一個函式返回一個 Promise,則表示該函式呼叫的結果不可用。當使用函式返回的 Promise 可用時,我們無法訪問實際輸出。
Promise 可以是以下三種狀態之一。
- 第一個狀態稱為待定狀態。當一個 Promise 被建立時,它將處於掛起狀態。
- 第二種稱為 Resolved 狀態,在這種狀態下 Promise 被成功執行
- 如果 Promise 發生任何錯誤,它將進入第三個狀態,稱為 Rejected。
語法:
new promise(function(resolve,reject){
//our logic goes here
});
在 TypeScript 中返回一個 Promise
使用 Promise 處理多個並行呼叫。使用它的主要優點是我們可以在不執行最後一行的情況下繼續執行下一行程式碼。
這也有助於提高應用程式的效能。
讓我們看看 Promise 的不同結果。
在 Promise 中拒絕和解決
為了管理 Promise 的錯誤響應,我們必須拒絕我們在回撥函式中提供的引數。這個拒絕引數將使用 catch() 塊處理錯誤。
語法:
function mypromise() { var promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) =>
{
// our logic goes here ..
reject();
}
mypromise().then(function(success)
{
// success logic will go here
})
.catch(function(error) { // logic goes here // });
我們還可以使用 resolve() 和一個成功的回撥來處理 Promise 函式的成功響應。
語法:
function demo()
{ var promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// logic will go here ..
resolve();
}
demo().then( () => // logic goes here .. );
為了更好地理解 TypeScript 中 Promise 的流程,讓我們看一下簡短的程式碼示例。
如果它被解決,Promise 將使用 .then(),如果它被拒絕,則使用 .catch()。
const promiseTypeScript = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("abc");
});
promiseTypeScript.then((res) => {
console.log('I get called:', res === 123); // I get called: true
});
promiseTypeScript.catch((err) => {
// This is never called
});
在上面的例子中,Promise 的 resolve() 部分被呼叫並返回一個布林值,而 reject() 部分不是。因此,此 Promise 將始終得到解決。
由於呼叫了 Promise 的 resolve() 部分,它將執行 .then()。
輸出:
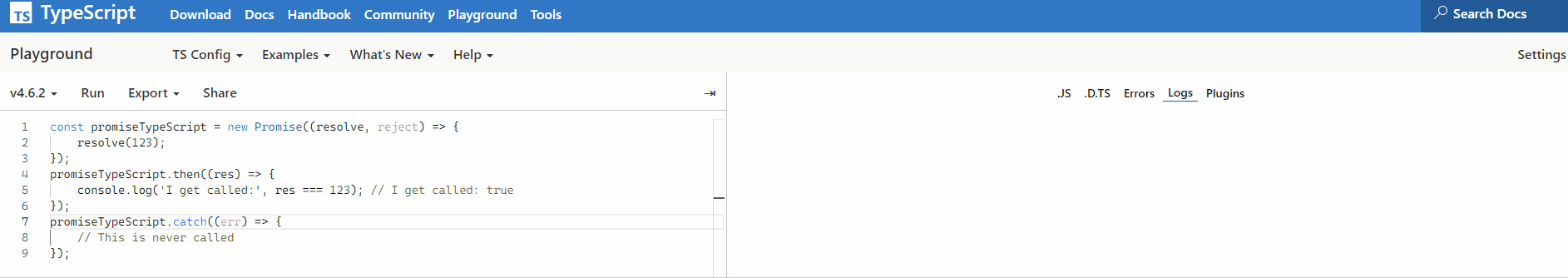
Promise 的 reject() 部分在以下程式碼中被呼叫,因為它總是返回錯誤。因此,.catch() 將被執行。
const promiseReturn = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(new Error("Something awful happened"));
});
promiseReturn.then((res) => {
// This is never called
});
promiseReturn.catch((err) => {
console.log('I get called:', err.message); // I get called: 'Something awful happened'
});
輸出:
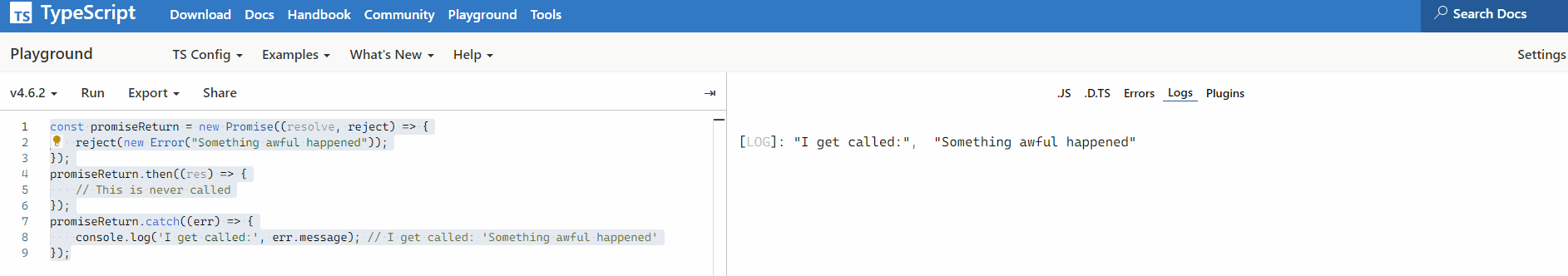
在 TypeScript 中,Promise 鏈能力是 Promise 好處的核心。使用 .then() 函式建立一個 Promise 鏈。
Promise.resolve(123)
.then((res) => {
console.log(res); // 123
return 456;
})
.then((res) => {
console.log(res); // 456
return Promise.resolve(123); // Notice that we are returning a Promise
})
.then((res) => {
console.log(res); // 123 : Notice that this `then` is called with the resolved value
return 123;
})
輸出:
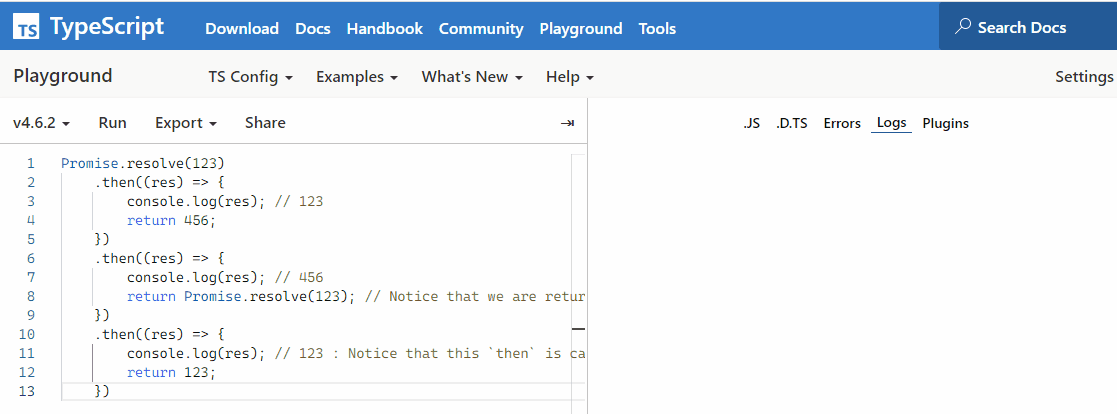
可以聚合單個 .catch() 用於鏈的任何前面部分的錯誤處理。
Promise.reject(new Error('something bad happened'))
.then((res) => {
console.log(res); // not called
return 456;
})
.then((res) => {
console.log(res); // not called
return 123;
})
.then((res) => {
console.log(res); // not called
return 123;
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log(err.message); // something bad happened
});
輸出:
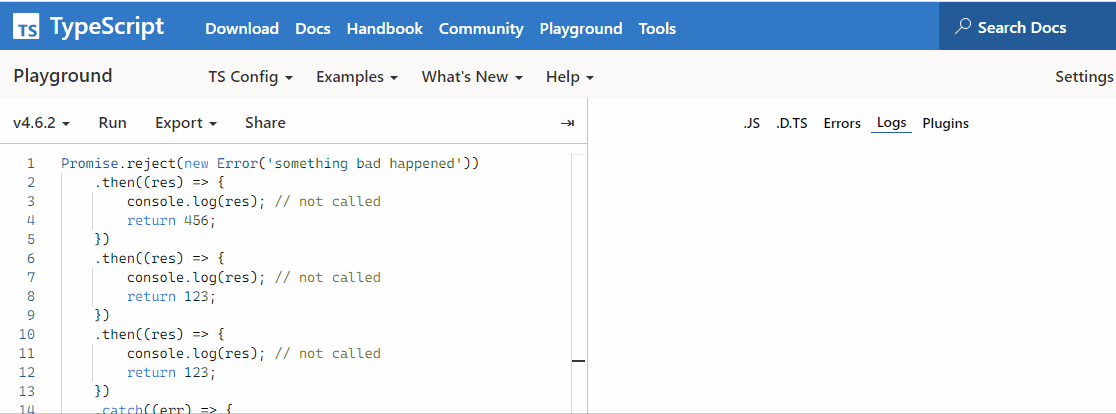
概括
- Promise 用於進行非同步呼叫。
- 請記住,你只能從不相互依賴的任務中呼叫。否則會出現資料不一致的問題。
- 使用時,必須通過 inner 函式;否則,你會得到一個錯誤。
Ibrahim is a Full Stack developer working as a Software Engineer in a reputable international organization. He has work experience in technologies stack like MERN and Spring Boot. He is an enthusiastic JavaScript lover who loves to provide and share research-based solutions to problems. He loves problem-solving and loves to write solutions of those problems with implemented solutions.
LinkedIn