防止 Java 中的 Orphaned Case 錯誤
- Java 中的 Orphaned Case 錯誤
-
Java 中避免
switch大小寫錯誤的最佳實踐 -
使用 Java
Scanner輸入流獲取使用者輸入 -
在 Java 中使用
Scanner獲取使用者輸入並應用switch案例 -
Java 中在
switch中使用while迴圈重複獲取使用者資料

本文解釋瞭如何防止 Java switch 語句中的孤立大小寫錯誤。它將在示例中演示 switch 案例,並使用 Scanner 輸入流使示例更加動態。
Java 中的 Orphaned Case 錯誤
在 Java 中,孤立錯誤並不常見。它與 switch 語句一起出現。
常見錯誤及解決方法:
Scanner 無法解析為型別。- 如果你的編譯器丟擲此錯誤,則意味著你必須匯入:import java.util.Scanner;來使用這個功能。java.util.InputMismatchException- 如果檢索到的令牌與指定型別的序列不匹配,或者如果令牌超出預期型別的範圍,Scanner將丟擲此錯誤。
Java 中避免 switch 大小寫錯誤的最佳實踐
我們將語法示例放在以下程式碼塊中,以避免所有 switch 語句的錯誤。
不正確:
Switch(demo);
{
Case(demo);
Case;
switch 情況時,切勿使用大寫字母。始終使用小寫字母以避免最常見的錯誤。正確的:
switch (demo) {
case 1: // for integer type
case "String": // for string type
; 在 switch() 和 case 語句之後。在 case 後始終使用冒號 :,在按鈕後不使用任何內容。最佳實踐:
- 你的
case應該在你的switch語句中。 - 永遠不要在
case語句中應用條件。 - 宣告一個型別,然後將它傳遞給你的
switch。不要指望switch自行確定你的型別。
程式碼:
// Int Example
int num = 0;
switch (num) {
case 1: // your code
break; // if the condition is true, the case breaks
}
// String Example
String str = "A";
switch (str) {
case "str": // our code
// break;
}
讓我們用 switch 案例製作出色的程式,同時避免罕見的孤立錯誤,如果現在很清楚的話。
使用 Java Scanner 輸入流獲取使用者輸入
以下是你應該瞭解的一些其他方法和引數,以充分理解此示例。
Scanner- 建立一個新的Scanner掃描提供的輸入流並返回值。next();- 此Scanner查詢並返回下一個完整標記("")。nextInt();- 它將輸入的下一個標記掃描為int。
引數:要掃描的資料流。
語法:
import java.util.Scanner;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Extend Scanner in Java
Scanner demo = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Print Something");
String a = demo.next(); // used for string
int b = demo.nextInt(); // used for integers
}
//(System.in): Theinput stream.
我們只是在 Scanner 的幫助下獲取輸入流並將其分配給 demo 變數。
在 Java 中使用 Scanner 獲取使用者輸入並應用 switch 案例
示例 1:
// example1
package AvoidError;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PreventOrphanedCaseErrorExample1 {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner demo = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("A");
System.out.println("B");
System.out.println("C");
System.out.println("D");
String a = demo.next();
switch (a) {
case "A":
System.out.println("You chose A");
break;
case "B":
System.out.println("You chose B");
break;
case "C":
System.out.println("You chose C");
break;
case "D":
System.out.println("You chose A");
break;
default:
System.out.println("You did not choose any value!");
break;
}
}
}
輸出:

Java 中在 switch 中使用 while 迴圈重複獲取使用者資料
這個例子的不同之處只是一種更動態的方法,我們還將使用 equals(); 方法,它比較字串。
如果 true,則返回給定物件;否則,它返回 false。仔細檢查以下程式碼。
示例 2:
// Example 2
package AvoidError;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PreventOrphanedCaseErrorExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (Scanner nxt = new Scanner(System.in)) {
while (true) {
System.out.println("1: Fruits");
System.out.println("2: Vegies");
System.out.println("3: Chicken");
System.out.println("Please select your choice!");
String i = nxt.next();
switch (i) {
case "1":
System.out.println("You chose Fruits");
break;
case "2":
System.out.println("You chose Vegies");
break;
case "3":
System.out.println("You chose Chicken");
break;
default:
System.out.println("Sorry! You did not choose from given options");
}
System.out.println("Do you want to repeat this operation?");
String REPEAT = nxt.next();
if (!REPEAT.equals("YES")) {
break;
}
}
}
}
}
輸出:
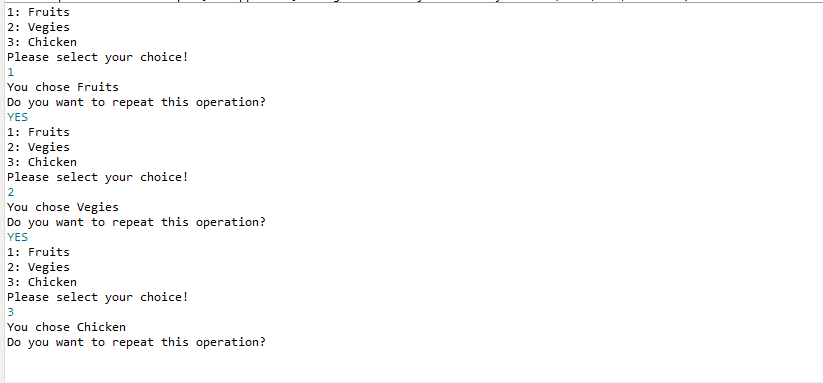
equals(); 之外,此示例中的所有內容都與前面的程式相同。我們儲存了 nxt.next(); 在字串 REPEAT 中,然後設定一個簡單的條件來檢查 equals(); 函式返回 true。在這種情況下,它返回字串的 YES;因此,我們在 switch 語句中使用點得到了一個更加動態的程式。
通過這種理解,你可以使用一些 Java 和 switch 語句函式來做任何事情。
Sarwan Soomro is a freelance software engineer and an expert technical writer who loves writing and coding. He has 5 years of web development and 3 years of professional writing experience, and an MSs in computer science. In addition, he has numerous professional qualifications in the cloud, database, desktop, and online technologies. And has developed multi-technology programming guides for beginners and published many tech articles.
LinkedIn