Como verificar se um valor existe na lista Python de uma forma rápida
- Método para verificar a existência do valor na lista Python
- Converter lista para definir e depois fazer a verificação de membros em Python
- Comparação de desempenho entre a lista e a verificação de associação a um set
Vamos introduzir métodos diferentes para verificar se um valor existe na lista Python e comparar a sua performance.
Os métodos incluem,
- Método de verificação de associação -
inMethod para verificar se o valor existe - Converter lista para
sete depois utilizar o método de verificação de associaçãoin.
Método para verificar a existência do valor na lista Python
é a maneira apropriada de fazer a verificação de membros na lista Python, conjunto, dicionário ou outros objetos iteráveis Python.
>>> testList = [1, 2, 3, 4]
>>> 2 in testList
True
>>> 6 in testList
False
Converter lista para definir e depois fazer a verificação de membros em Python
A verificação dos membros na lista pode ser ineficiente se o tamanho da lista aumentar, especialmente se existirem elementos duplicados na lista.
O array Python é um tipo de dados melhor neste cenário para fazer a verificação de associação, pois contém apenas valores únicos.
Comparação de desempenho entre a lista e a verificação de associação a um set
Iremos comparar as diferenças de desempenho em quatro situações,
- A lista original tem valores únicos, e o valor verificado existe na lista
- A lista original tem valores únicos, e o valor verificado não existe na lista.
- A lista original tem valores duplicados, e o valor verificado existe na lista
- A lista original tem apenas valores duplicados, e o valor verificado não existe na lista.
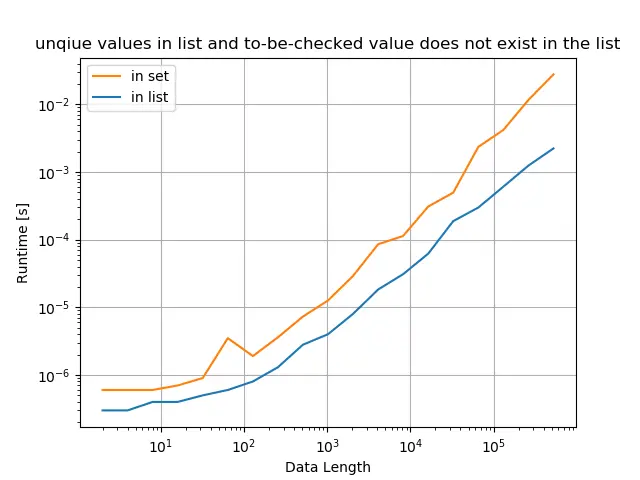
A lista original tem apenas valores únicos, e o valor verificado existe na lista
from itertools import chain
import perfplot
import numpy as np
def setupTest(n):
a = np.arange(n)
np.random.shuffle(a)
randomlist = a[: n // 2].tolist()
randomvalue = randomlist[len(randomlist) // 2]
return [randomlist, randomvalue]
def inListMethod(L):
x, y = L
return y in x
def inSetMethod(L):
x, y = L
x = set(x)
return y in x
perfplot.show(
setup=setupTest,
kernels=[inListMethod, inSetMethod],
labels=["in list", "in set"],
n_range=[2 ** k for k in range(1, 20)],
xlabel="Data Length",
title="unique values in list and to-be-checked value exists in the list",
logx=True,
logy=True,
)
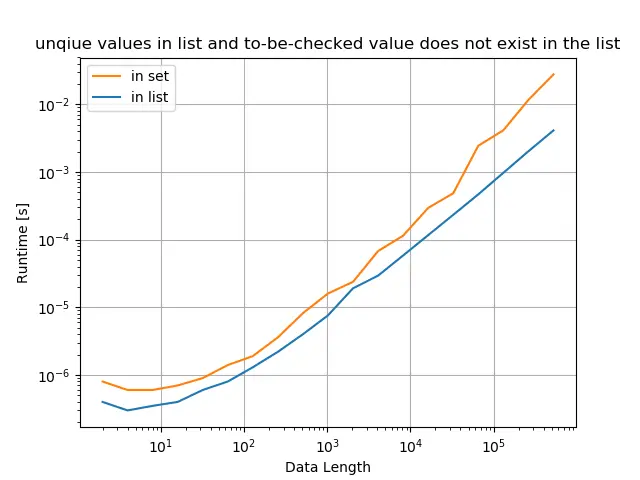
A lista original tem apenas valores únicos, e o valor verificado não existe na lista
from itertools import chain
import perfplot
import numpy as np
def setupTest(n):
a = np.arange(n)
np.random.shuffle(a)
randomlist = a[: n // 2].tolist()
randomvalue = n + 1
return [randomlist, randomvalue]
def inListMethod(L):
x, y = L
return y in x
def inSetMethod(L):
x, y = L
x = set(x)
return y in x
perfplot.show(
setup=setupTest,
kernels=[inListMethod, inSetMethod],
labels=["in list", "in set"],
n_range=[2 ** k for k in range(1, 20)],
xlabel="Data Length",
title="unique values in list and to-be-checked value does not exist in the list",
logx=True,
logy=True,
)
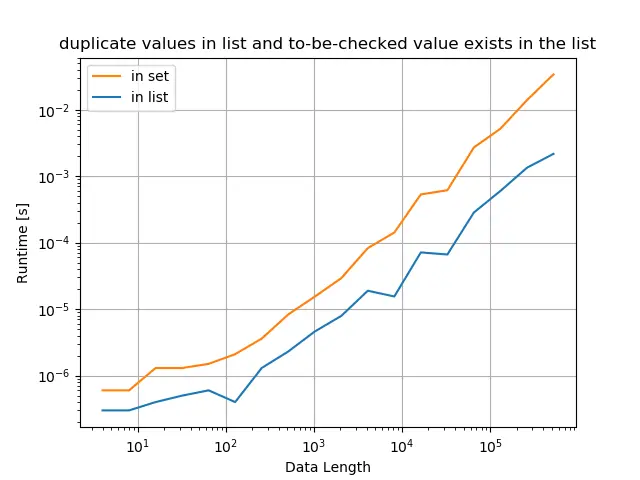
A lista original tem valores duplicados, e o valor verificado existe na lista
from itertools import chain
import perfplot
import numpy as np
def setupTest(n):
a = np.arange(n)
np.random.shuffle(a)
randomlist = np.random.choice(n, n // 2).tolist()
randomvalue = randomlist[len(randomlist) // 2]
return [randomlist, randomvalue]
def inListMethod(L):
x, y = L
return y in x
def inSetMethod(L):
x, y = L
x = set(x)
return y in x
perfplot.show(
setup=setupTest,
kernels=[inListMethod, inSetMethod],
labels=["in list", "in set"],
n_range=[2 ** k for k in range(2, 20)],
xlabel="Data Length",
title="duplicate values in list and to-be-checked value exists in the list",
logx=True,
logy=True,
)
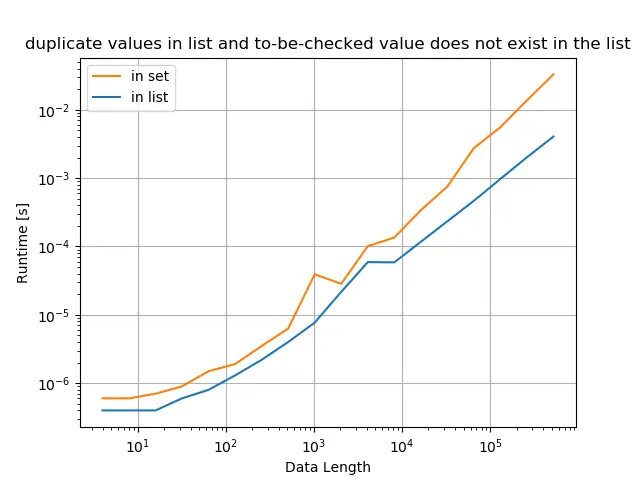
A lista original tem apenas valores duplicados, e o valor verificado não existe na lista
from itertools import chain
import perfplot
import numpy as np
def setupTest(n):
a = np.arange(n)
np.random.shuffle(a)
randomlist = np.random.choice(n, n // 2).tolist()
randomvalue = n + 1
return [randomlist, randomvalue]
def inListMethod(L):
x, y = L
return y in x
def inSetMethod(L):
x, y = L
x = set(x)
return y in x
perfplot.show(
setup=setupTest,
kernels=[inListMethod, inSetMethod],
labels=["in list", "in set"],
n_range=[2 ** k for k in range(2, 20)],
xlabel="Data Length",
title="duplicate values in list and to-be-checked value does not exist in the list",
logx=True,
logy=True,
)
Conclusão da Comparação de Desempenho
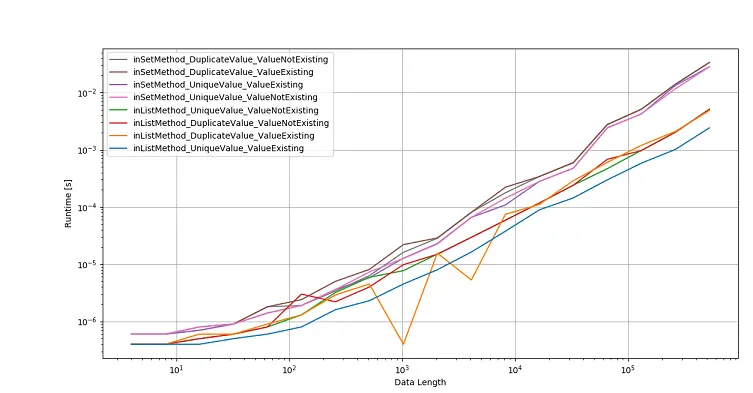
Embora a verificação de associação em Python set seja mais rápida do que na lista Python, a conversão de lista ou set consome tempo. Portanto, se os dados fornecidos são a lista Python, não tem nenhum benefício de performance se você primeiro converter a lista para set e depois fazer a verificação de associação em set.
from itertools import chain
import perfplot
import numpy as np
def setupTest(n):
a = np.arange(n)
np.random.shuffle(a)
unique_randomlist = a[: n // 2].tolist()
duplicate_randomlist = np.random.choice(n, n // 2).tolist()
existing_randomvalue = unique_randomlist[len(unique_randomlist) // 2]
nonexisting_randomvalue = n + 1
return [
unique_randomlist,
duplicate_randomlist,
existing_randomvalue,
nonexisting_randomvalue,
]
def inListMethod_UniqueValue_ValueExisting(L):
u, d, ex, ne = L
return ex in u
def inListMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueExisting(L):
u, d, ex, ne = L
return ex in d
def inListMethod_UniqueValue_ValueNotExisting(L):
u, d, ex, ne = L
return ne in u
def inListMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueNotExisting(L):
u, d, ex, ne = L
return ne in d
def inSetMethod_UniqueValue_ValueExisting(L):
u, d, ex, ne = L
u = set(u)
return ex in u
def inSetMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueExisting(L):
u, d, ex, ne = L
d = set(d)
return ex in d
def inSetMethod_UniqueValue_ValueNotExisting(L):
u, d, ex, ne = L
u = set(u)
return ne in u
def inSetMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueNotExisting(L):
u, d, ex, ne = L
d = set(d)
return ne in d
perfplot.show(
setup=setupTest,
equality_check=None,
kernels=[
inListMethod_UniqueValue_ValueExisting,
inListMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueExisting,
inListMethod_UniqueValue_ValueNotExisting,
inListMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueNotExisting,
inSetMethod_UniqueValue_ValueExisting,
inSetMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueExisting,
inSetMethod_UniqueValue_ValueNotExisting,
inSetMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueNotExisting,
],
labels=[
"inListMethod_UniqueValue_ValueExisting",
"inListMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueExisting",
"inListMethod_UniqueValue_ValueNotExisting",
"inListMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueNotExisting",
"inSetMethod_UniqueValue_ValueExisting",
"inSetMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueExisting",
"inSetMethod_UniqueValue_ValueNotExisting",
"inSetMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueNotExisting",
],
n_range=[2 ** k for k in range(2, 20)],
xlabel="Data Length",
logx=True,
logy=True,
)
Founder of DelftStack.com. Jinku has worked in the robotics and automotive industries for over 8 years. He sharpened his coding skills when he needed to do the automatic testing, data collection from remote servers and report creation from the endurance test. He is from an electrical/electronics engineering background but has expanded his interest to embedded electronics, embedded programming and front-/back-end programming.
LinkedIn Facebook