Python Numpy.sqrt() - Radice quadrata
-
Sintassi di
numpy.sqrt() -
Codici di esempio:
numpy.sqrt() -
Codici di esempio:
numpy.sqrt()senza parametroout -
Codici di esempio:
numpy.sqrt()con numeri negativi -
Codici di esempio:
numpy.sqrt()con numeri complessi

La funzione Numpy.sqrt() calcola la radice quadrata di ogni elemento nell’array dato.
È l’operazione inversa del metodo Numpy.square().
Sintassi di numpy.sqrt()
numpy.sqrt(arr, out=None)
Parametri
arr |
matrice di input |
out |
Se viene fornito out, il risultato verrà memorizzato in out. out dovrebbe avere la stessa forma di arr. |
Ritorno
Restituisce un array della radice quadrata di ogni elemento nell’array di input, anche se viene fornito out.
Codici di esempio: numpy.sqrt()
import numpy as np
arr = [1, 9, 25, 49]
arr_sqrt = np.sqrt(arr)
print(arr_sqrt)
Produzione:
[1. 3. 5. 7.]
Codici di esempio: numpy.sqrt() senza parametro out
import numpy as np
arr = [1, 9, 25, 49]
out_arr = np.zeros(4)
arr_sqrt = np.sqrt(arr, out_arr)
print(out_arr)
print(arr_sqrt)
Produzione:
[1. 3. 5. 7.]
[1. 3. 5. 7.]
out_arr ha la stessa forma di arr, e la radice quadrata di arr viene salvata al suo interno. E il metodo numpy.sqrt() restituisce anche l’array della radice quadrata, come mostrato sopra.
Se out non ha la stessa forma di arr, solleva un ValueError.
import numpy as np
arr = [1, 9, 25, 49]
out_arr = np.zeros((2, 2))
arr_sqrt = np.sqrt(arr, out_arr)
print(out_arr)
print(arr_sqrt)
Produzione:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Test\test.py", line 6, in <module>
arr_sqrt = np.sqrt(arr, out_arr)
ValueError: operands could not be broadcast together with shapes (4,) (2,2)
Codici di esempio: numpy.sqrt() con numeri negativi
import numpy as np
arr = [-1, -9, -25, -49]
arr_sqrt = np.sqrt(arr)
print(arr_sqrt)
Produzione:
Warning (from warnings module):
File "..\test.py", line 5
arr_sqrt = np.sqrt(arr)
RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in sqrt
[nan nan nan nan]
Genera un RuntimeWarning quando l’input è un numero negativo e restituisce come risultato nan.
Codici di esempio: numpy.sqrt() con numeri complessi
import numpy as np
arr = [3 + 4j, -5 + 12j, 8 - 6j, -15 - 8j]
arr_sqrt = np.sqrt(arr)
print(arr_sqrt)
Produzione:
[2.+1.j 2.+3.j 3.-1.j 1.-4.j]
Un numero complesso ha due radici quadrate. Per esempio,
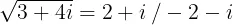
Il metodo numpy.sqrt() restituisce solo una radice quadrata, che ha un numero reale positivo.
Founder of DelftStack.com. Jinku has worked in the robotics and automotive industries for over 8 years. He sharpened his coding skills when he needed to do the automatic testing, data collection from remote servers and report creation from the endurance test. He is from an electrical/electronics engineering background but has expanded his interest to embedded electronics, embedded programming and front-/back-end programming.
LinkedIn Facebook