Utilice la condición si no en Python
La declaración if se combina con el operador lógico not para evaluar si una condición no sucedió. Este artículo explica cómo utilizar la condición if not en Python.
Aquí hay un bloque de código que demuestra esta condición.
if not a_condition:
block_of_code_to_execute_if_condition_is_false
En el caso anterior, el código block_of_code_to_execute_if_condition_is_false se ejecutará con éxito si el resultado de a_condition es False.
Valores verdaderos y falsos en Python
Antes de comenzar, entendamos que el valor equivalente es False en Python en los siguientes casos:
- Valores cero numéricos, como
0,0L,0.0 - Secuencias vacías como:
- lista vacía []
- diccionario vacío {}
- cuerda vacía ''
- tupla vacía
- conjunto vacio
- un objeto
None
Ejemplos de la condición if not en Python
Aquí hay varios ejemplos que le ayudarán a comprender cómo se utiliza if not en Python.
Uso de valores booleanos
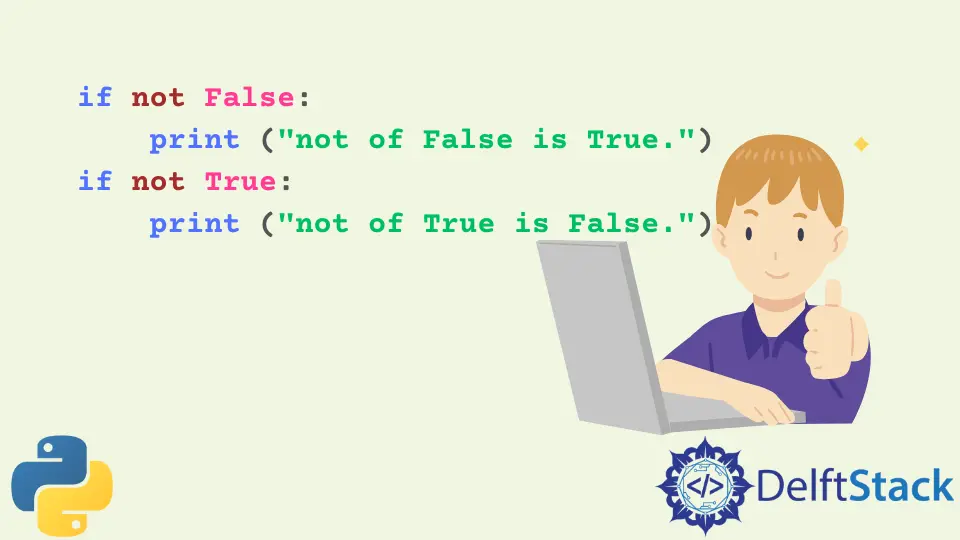
if not False:
print("not of False is True.")
if not True:
print("not of True is False.")
Producción :
not of False is True.
Uso de un valor numérico
Por ejemplo, valores como 0, 0L, 0.0 se asocian con el valor False.
if not 0:
print("not of 0 is True.")
if not 1:
print("not of 1 is False.")
Producción :
not of 0 is True.
Uso de la lista de valores
if not []:
print("An empty list is false. Not of false =true")
if not [1, 2, 3]:
print("A non-empty list is true. Not of true =false")
Producción :
An empty list is false. Not of false =true
Uso de valores de diccionario
if not {}:
print("An empty dictionary dict is false. Not of false =true")
if not {"vehicle": "Car", "wheels": "4", "year": 1998}:
print("A non-empty dictionary dict is true. Not of true =false")
Producción :
An empty dictionary dict is false. Not of false =true
Uso de String de valores
if not "":
print("An empty string is false. Not of false =true")
if not "a string here":
print("A non-empty string is true. Not of true =false")
Producción :
An empty string is false. Not of false =true
Uso de un valor None:
if not None:
print("None is false. Not of false =true")
Producción :
None is false. Not of false =true
Uso de set de valores:
dictvar = {}
print("The empty dict is of type", type(dictvar))
setvar = set(dictvar)
print("The empty set is of type", type(setvar))
if not setvar:
print("An empty set is false. Not of false =true")
Producción :
The empty dict is of type <class 'dict'>
The empty set is of type <class 'set'>
An empty dictionary dict is false. Not of false =true
Uso de una tuple de valores
Una tupla vacía se asocia con el valor False.
if not ():
print("1-An empty tuple is false. Not of false =true")
if not tuple():
print("2-An empty tuple is false. Not of false =true")
Producción :
1-An empty tuple is false. Not of false =true
2-An empty tuple is false. Not of false =true