連結串列插入
Harshit Jindal
2024年2月15日
Data Structure
Linked List
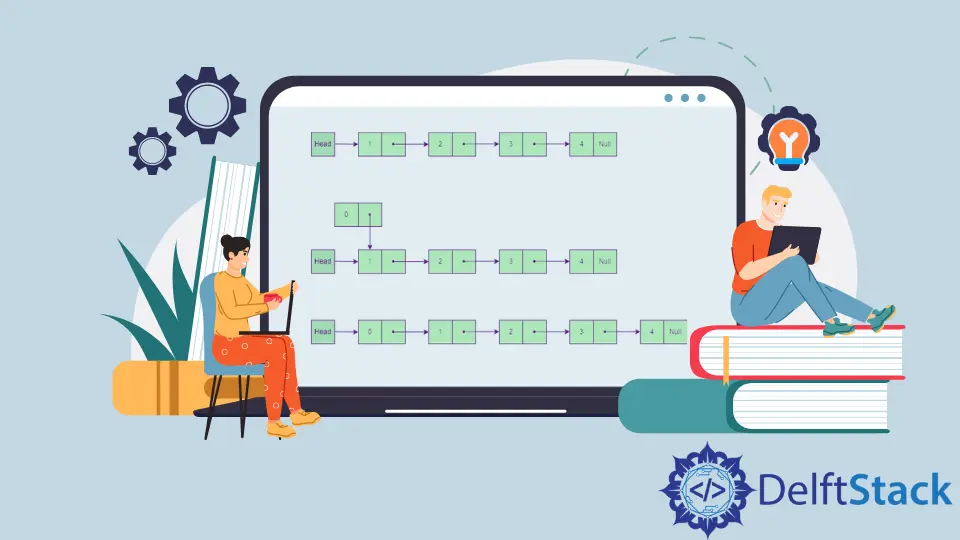
在本文中,我們將學習如何在連結串列中插入節點。我們可以看到出現了 4 種不同的情況。
- 我們要在連結列表的開頭之前插入一個節點。此操作類似於堆疊中的推入操作。
- 我們要在連結列表的末尾(即尾節點旁邊)插入一個節點。
- 我們想在連結列表的第 i 個位置插入一個節點。
- 我們有該節點的引用,之後我們要插入新節點。
連結串列插入演算法
令 head 為指向連結串列第一個節點的指標,令 x 為要插入連結串列中的資料。
在連結列表 push() 的開頭插入節點
-
用資料
x建立一個新節點temp。 -
將
temp->next設定為head,以在head之前插入temp。 -
將
temp設定為連結列表的開頭。
在連結列表 append() 的末尾插入節點
-
用資料
x建立一個新節點temp。 -
初始化指向
head的tail。 -
如果連結列表為空,則將
temp設定為連結列表的head,然後返回。 -
否則,迭代連結列表的末尾,使
tail->next!=NULL,以便你到達最後一個元素 -
將
tail->next設定為temp。
在連結列表 insertNpos() 的 i-th 位置處插入節點
-
如果位置
pos<=0,則返回;否則返回 0。 -
如果
pos==0並且head為空,則建立一個資料為x的新節點並將其設定為head。 -
如果
pos==1,則呼叫push()。 -
另外,用資料
x建立一個新節點temp。 -
初始化指向
head的curr。 -
當
pos--時,執行以下操作。-
如果
pos==1,- 如果
curr不是NULL- 將
temp->next設定為curr->next,以便在curr之後插入temp。 - 將
curr->next設定為temp,以將curr連線到temp。
- 將
- 返回;
- 如果
-
否則將
curr設定為curr->next。
-
在給定節點的引用旁邊插入節點 - insertAfter()
-
如果
prev==NULL,則返回; -
用資料
x建立一個新節點curr。 -
將
curr->next指向prev->next以在 prev 之後新增新節點。 -
將
prev->next指向curr以完成插入。
連結串列插入圖
假設我們有一個節點 temp,其資料值等於 5,我們想將其插入連結串列中。讓我們考慮所有 4 種情況,並說明上述演算法是如何工作的。
在連結列表的開頭插入節點 - push()
-
將
temp的指標設定為head。 -
將
head指向temp。
在連結列表 append() 的末尾插入節點
-
將
curr指向head,資料為2。 -
將
curr設定為curr->next,並將其移動到資料為3的節點。 -
將
curr設定為curr->next,並將其移動到資料為4的節點。 -
退出 while 迴圈並將
curr->next設定為temp。
在連結列表的 i-th 位置處插入節點 - insertNpos()
我們將節點插入到位置 3。
-
將
curr指向head,資料為1,pos=pos-1=2。 -
將
curr設定為curr->next,並將其移動到資料為3,pos=pos -1=1的節點。 -
將
temp->next設定為curr->next,以便在curr之後插入 temp。 -
將
curr->next設定為temp,以在curr和curr->next之間完成temp的插入。
在給定節點 insertAfter() 的引用旁邊插入節點
-
將
temp->next設定為prev->next,以在prev和prev->next之間插入temp。 -
將
prev->next設定為temp以完成插入。
連結串列插入實現
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
Node(int x) {
this->data = x;
this->next = NULL;
}
};
void push(Node** head, int x) {
Node* temp = new Node(x);
temp->next = (*head);
(*head) = temp;
}
void insertAfter(Node* prev, int x) {
if (prev == NULL) {
return;
}
Node* curr = new Node(x);
curr->next = prev->next;
prev->next = curr;
}
void printList(Node* head) {
Node* curr = head;
while (curr != NULL) {
cout << curr->data << " ";
curr = curr->next;
}
}
void insertNpos(Node** head, int x, int pos) {
if (pos <= 0) {
return;
}
if (!head && pos == 1) {
*head = new Node(x);
} else if (pos == 1) {
push(head, x);
}
Node* temp = new Node(x);
Node* curr = *head;
while (pos--) {
if (pos == 1) {
if (curr) {
temp->next = curr->next;
curr->next = temp;
}
return;
}
curr = curr->next;
}
}
void append(Node** head, int x) {
Node* temp = new Node(x);
Node* tail = *head;
if (*head == NULL) {
*head = temp;
return;
}
while (tail->next != NULL) tail = tail->next;
tail->next = temp;
return;
}
int main() {
Node* head = new Node(1);
head->next = new Node(2);
printList(head);
cout << "\n";
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 4);
printList(head);
cout << "\n";
append(&head, 5);
printList(head);
cout << "\n";
insertAfter(head->next->next, 6);
printList(head);
cout << "\n";
insertNpos(&head, 24, 2);
printList(head);
return 0;
}
連結串列插入演算法的複雜度
時間複雜度
- 平均情況
要將節點插入連結串列中的第 i 個位置,我們必須訪問 i 個節點。因此,時間複雜度約為 O(i)。而且我們在連結串列中有 n 個節點,因此平均情況下的時間複雜度為 O(n/2) 或 O(n)。時間複雜度約為 O(n)。
- 最佳情況
最好的情況是,當我們想在連結串列的開頭插入一個節點,或者在插入站點之前有對該節點的引用時。最佳情況下的時間複雜度是 O(1)。
- 最壞情況
最差的時間複雜度是 O(n)。這與平均情況下的時間複雜度相同。
空間複雜度
該插入演算法的空間複雜度為 O(1),因為除 curr 指標外不需要其他空間。
Enjoying our tutorials? Subscribe to DelftStack on YouTube to support us in creating more high-quality video guides. Subscribe
作者: Harshit Jindal
Harshit Jindal has done his Bachelors in Computer Science Engineering(2021) from DTU. He has always been a problem solver and now turned that into his profession. Currently working at M365 Cloud Security team(Torus) on Cloud Security Services and Datacenter Buildout Automation.
LinkedIn



