C 語言中的雙指標**

本教程教授如何使用指向指標的指標(雙指標或**)來儲存另一個指標變數的地址。
C 語言中變數的記憶體分配
在建立變數時,將分配一些特定的記憶體塊給該變數用於儲存值。例如,我們建立了一個 char 變數 ch 和值 a。在內部,一個位元組的記憶體將分配給變數 ch。

C 指標
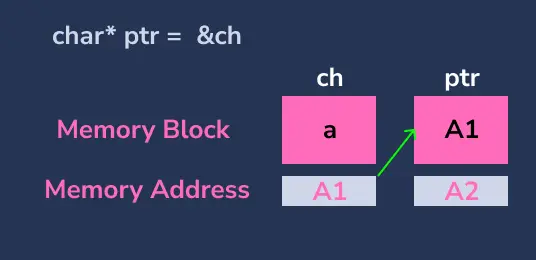
在 C 程式設計中,指標是儲存另一個變數地址的變數。要訪問該地址中存在的值,我們使用*。
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char ch = 'a'; // create a variable
char *ptr = &ch; // create a pointer to store the address of ch
printf("Address of ch: %p\n", &ch); // prints address
printf("Value of ch: %c\n", ch); // prints 'a'
printf("\nValue of ptr: %p\n", ptr); // prints the address of a
printf("*ptr(value of ch): %c\n",
*ptr); // Prints Content of the value of the ptr
}
輸出:
Address of ch: 0x7ffc2aa264ef
Value of ch: a
Value of ptr: 0x7ffc2aa264ef
*ptr(value of ch): a
在上面的程式碼中,
- 建立一個
char變數ch並將字元a分配為一個值。 - 建立一個
char指標ptr並儲存變數ch的地址。 - 列印
ch的地址和值。 - 列印
ptr的值,ptr的值將是ch的地址 - 使用
*ptr列印ch的值。ptr的值是變數ch的地址,在該地址中存在值'a',因此將列印它。
C 語言中指向指標的指標(**)
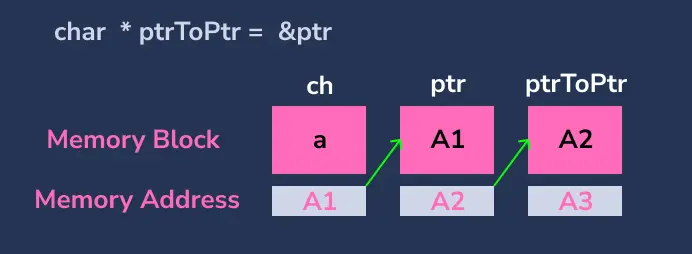
為了儲存變數的地址,我們使用指標。同樣,要儲存指標的地址,我們需要使用(指向指標的指標)。 表示儲存另一個指標地址的指標。
要列印指向指標變數的指標中的值,我們需要使用**。
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char ch = 'a'; // create a variable
char *ptr = &ch; // create a pointer to store the address of ch
char **ptrToPtr = &ptr; // create a pointer to store the address of ch
printf("Address of ch: %p\n", &ch); // prints address of ch
printf("Value of ch: %c\n", ch); // prints 'a'
printf("\nValue of ptr: %p\n", ptr); // prints the address of ch
printf("Address of ptr: %p\n", &ptr); // prints address
printf("\nValue of ptrToPtr: %p\n", ptrToPtr); // prints the address of ptr
printf("*ptrToPtr(Address of ch): %p\n",
*ptrToPtr); // prints the address of ch
printf("**ptrToPtr(Value of ch): %c\n", **ptrToPtr); // prints ch
}
輸出:
Address of ch: 0x7fffb48f95b7
Value of ch: a
Value of ptr: 0x7fffb48f95b7
Address of ptr: 0x7fffb48f95b8
Value of ptrToPtr: 0x7fffb48f95b8
*ptrToPtr(Address of ch): 0x7fffb48f95b7
**ptrToPtr(Value of ch): a
在上面的程式碼中,
- 建立一個
char變數ch並將字元a作為值分配給它。 - 建立一個
char指標ptr並儲存變數ch的地址。 - 建立一個指向指標
ptrToPtr的char指標並儲存變數ptr的地址。 - ptr 將以變數
ch的地址作為值,而ptrToPtr將以指標ptr的地址作為值。 - 當我們像
*ptrToPtr那樣取消引用ptrToPtr時,我們得到變數ch的地址 - 當我們像
**ptrToPtr那樣取消引用ptrToPtr時,我們得到變數ch的值
要記住的要點
為了儲存 ptrToPtr 的地址,我們需要建立
char ***ptrToPtrToPtr = &ptrToPtr;
printf("***ptrToPtrToPtr : %c\n", ***ptrToPtrToPtr); // 'a'
Enjoying our tutorials? Subscribe to DelftStack on YouTube to support us in creating more high-quality video guides. Subscribe